Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on May 2, 2024
What is the Lewis structure of carbonate ion CO32-?
To draw the Lewis structure of CO32–, we first need to determine the total number of valence electrons present in the molecule. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that participate in chemical bonding. In CO32-, we have one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms. Carbon has four valence electrons, while each oxygen atom has six valence electrons. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in CO32- is:
4 + (3 x 6) + 2 = 24
The extra two electrons are added to the total because the ion carries a -2 charge.
Next, we need to connect the atoms in the molecule using single or double bonds. Carbon can form four bonds, while oxygen can form two bonds. Therefore, we can place a double bond between the carbon atom and one of the oxygen atoms, and single bonds between the carbon atom and the remaining two oxygen atoms. This arrangement gives each oxygen atom a complete octet of electrons, while the carbon atom has only six electrons.
To complete the octet of the carbon atom, we can use one of the lone pairs on one of the oxygen atoms to form a double bond with carbon. This will give the carbon atom a complete octet of electrons, and each oxygen atom will still have a complete octet of electrons.
The final Lewis structure of CO32- can be represented as:
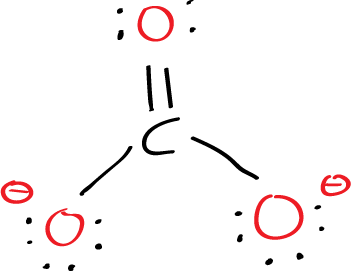
In this structure, the carbon atom is connected to three oxygen atoms, with one double bond and two single bonds. The remaining electrons are distributed as lone pairs on the oxygen atoms.
The negative charge on the ion is located on two of the oxygen atoms, to indicate that it has gained two electrons and achieved a stable octet configuration.
The Lewis structure of the carbonate ion provides important information about the chemical properties of the molecule. For example, it shows that the ion has a trigonal planar geometry, and that the oxygen atoms are negatively charged, while the carbon atom is positively charged. This information can be used to predict the behavior of carbonate ion in chemical reactions and its interactions with other molecules.
In conclusion, the Lewis structure of the carbonate ion is an important tool in understanding the chemical properties of the molecule. By knowing the arrangement of atoms and electrons in the molecule, we can predict how it will behave in different chemical reactions and interactions with other molecules.