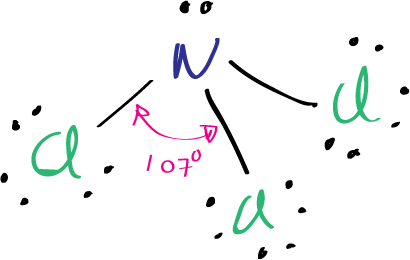Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on May 2, 2024
What is the Lewis structure of nitrogen trichloride NCl3 ?
Nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), also known as trichloramine, is a yellowish-green gas with a pungent odor that is used as a disinfectant and bleach. It is commonly used in swimming pools, wastewater treatment plants, and in the production of rubber and nylon.
The Lewis structure is a model used to show the bonding between atoms in a molecule. It is based on the idea that atoms form bonds in order to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically the same as that of the noble gas closest to it in the periodic table. The Lewis structure shows the valence electrons of each atom and how they are shared or transferred between the atoms in a molecule.
To draw the Lewis structure of nitrogen trichloride NCl3, we first need to determine the number of valence electrons in each atom. Nitrogen (N) is in group 5A of the periodic table and has five valence electrons, while chlorine (Cl) is in group 7A and has seven valence electrons. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons in nitrogen trichloride can be calculated as follows:
Number of valence electrons in N + Number of valence electrons in 3Cl = 5 + (3 × 7) = 26
The Lewis structure of nitrogen trichloride NCl3 can be drawn using this number of valence electrons. We begin by placing the nitrogen atom in the center and arranging the three chlorine atoms around it. Each chlorine atom is connected to the nitrogen atom by a single bond, and the remaining electrons are distributed to satisfy the octet rule, which states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons until they are surrounded by eight electrons (or two electrons for hydrogen).
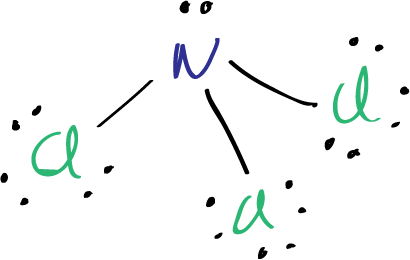
The Lewis structure of nitrogen trichloride NCl3 shows that there are three single bonds between the nitrogen and chlorine atoms, and that each chlorine atom has one lone pair of electrons. Nitrogen also has one lone pair of electrons.
The Lewis structure of nitrogen trichloride NCl3 shows that each atom has a full octet, with nitrogen and each chlorine atom having eight electrons around them, four of which are shared in covalent bonds. The molecule is trigonal pyramidal in shape, with the nitrogen atom at the apex and the three chlorine atoms forming a triangular base. The bond angles are approximately 107 degrees, and the molecule has a dipole moment due to the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and chlorine.