Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on May 2, 2024
What is the Lewis structure of nitrate ion NO3– ?
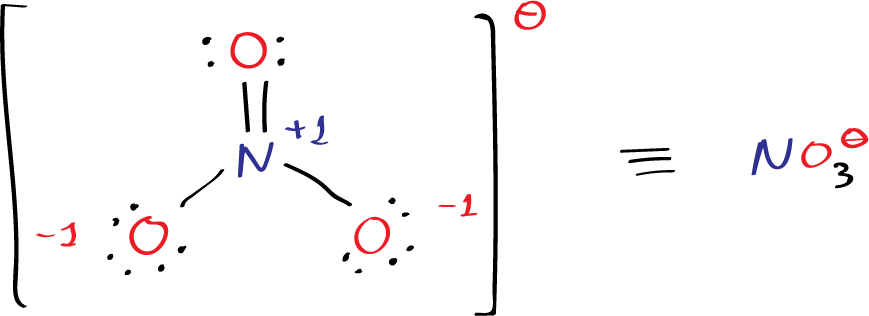
The nitrite ion is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula NO3–. It is composed of one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms, where the nitrogen atom has a formal charge of +1, and two oxygen atom has a formal charge of -1.
The Lewis structure of the nitrite ion represents the arrangement of electrons in the molecule, which is essential to understanding its chemical properties and reactivity.
Step by step Lewis structure of nitrate ion NO3–
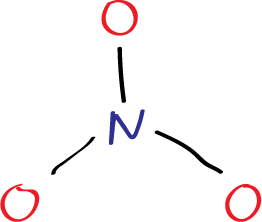
The first step in drawing the Lewis structure is to arrange the atoms in the molecule. Since nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, it is placed in the center, with the three oxygen atoms bonded to it.
Step 1: Firstly, a nitrogen atom is drawn surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement.
Also, to draw the Lewis structure of the nitrite ion, we need to determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding. Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, and each oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons, giving a total of 24 valence electrons for the nitrite ion (plus the -1 charge of the whole molecule).
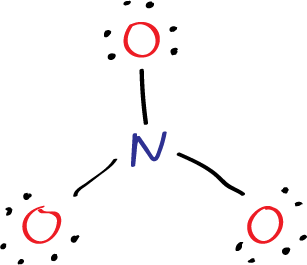
The nitrogen atom forms a single bond with three oxygen atoms and six electorns are added also (three lone pairs of electrons) on oxygen atoms.
Step 2: six electrons (three lone pairs) are added on each oxygen atom (representes as dots).
The nitrate ion is composed of one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms, with a charge of -1. Nitrogen and oxygen are located in the VA and VIA groups, respectively, on the periodic table. Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, while oxygen has 6 valence electrons in its valence shell.
To determine the total number of valence electrons in the nitrate ion, we need to consider the valence electrons of each atom. The nitrogen atom provides 5 valence electrons, and there are three oxygen atoms, each contributing 6 valence electrons. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons contributed by the oxygen atoms is 18.
Step3: calculate atomic charges as the diffence between the number of valence electrons and the counting of electrons and bonds. For example the upper oxygen in the figure has 6 dots and one single bond = 7 (6-7 = -1). The nitrogen has 5 valence electrons minus 3 single bonds 5-3 = +2. Negative numbers are represented in red and positive in blue with the corresponding sign.
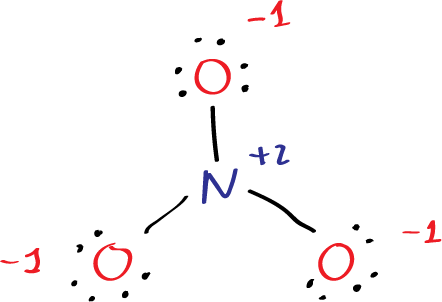
Since the nitrate ion carries a total charge of -1, one additional electron is added to the total valence electrons. Thus, the total number of valence electrons in the nitrate ion is 24 (5 from nitrogen, 18 from oxygen, and 1 from the additional electron due to the -1 charge).
The next step is to add the remaining electrons to the molecule. Since there are 24 valence electrons in the nitrite ion, we have eight electrons remaining after forming the bonds between nitrogen and oxygen. These eight electrons are added as lone pairs and a double bond to the oxygen atoms, completing their octets.
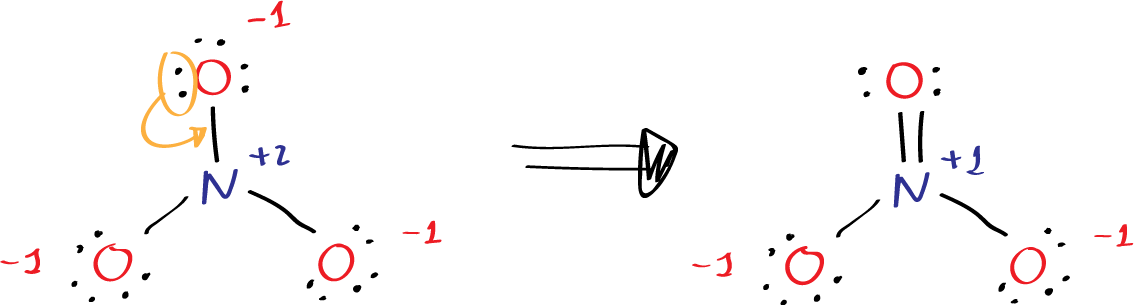
Step 4, we check the formal charges of each atom in the molecule to ensure that they are minimized. The formal charge is calculated by subtracting the number of lone pair electrons and half the number of bonding electrons from the number of valence electrons for each atom. In the nitrite ion, the nitrogen atom has a formal charge of +1, and two oxygen atoms have formal charge of -1, which adds up to the overall charge of -1 for the molecule. Therefore, in the figure we have to move two electrons from the oxygen to form a new N-O bonds and the charge at the nitrogen reduced to +1.
The Lewis structure of the nitrite ion is shown below:

The single bond between nitrogen and oxygen is represented by a single dash, and the lone pairs of electrons are represented by dots. The formal charges of each atom are shown as superscripts with the ⊖ symbol. The nitrate ion can also be enclosed in square brackets [ ].