What is fastening and anchoring?
To work safely in a laboratory of Organic Chemistry, it is essential that any type of container or assembly and its components are properly assembled and fixed on a support to prevent accidents. The most common devices that are used for this purpose in a laboratory are described below.
Ring stand
It is an essential element to maintain the glassware elements fixed and safe , while conducting an experiment. The supports are formed by a metal rods located upright, usually of stainless steel.
These supports are composed of intersecting horizontal and vertical metal rods, and are usually integrated into lab benches or metal supports formed by one or more metal rods, with the corresponding base that allows placing them in different locations. Clamps and clamp holders are attached to these ring stands.
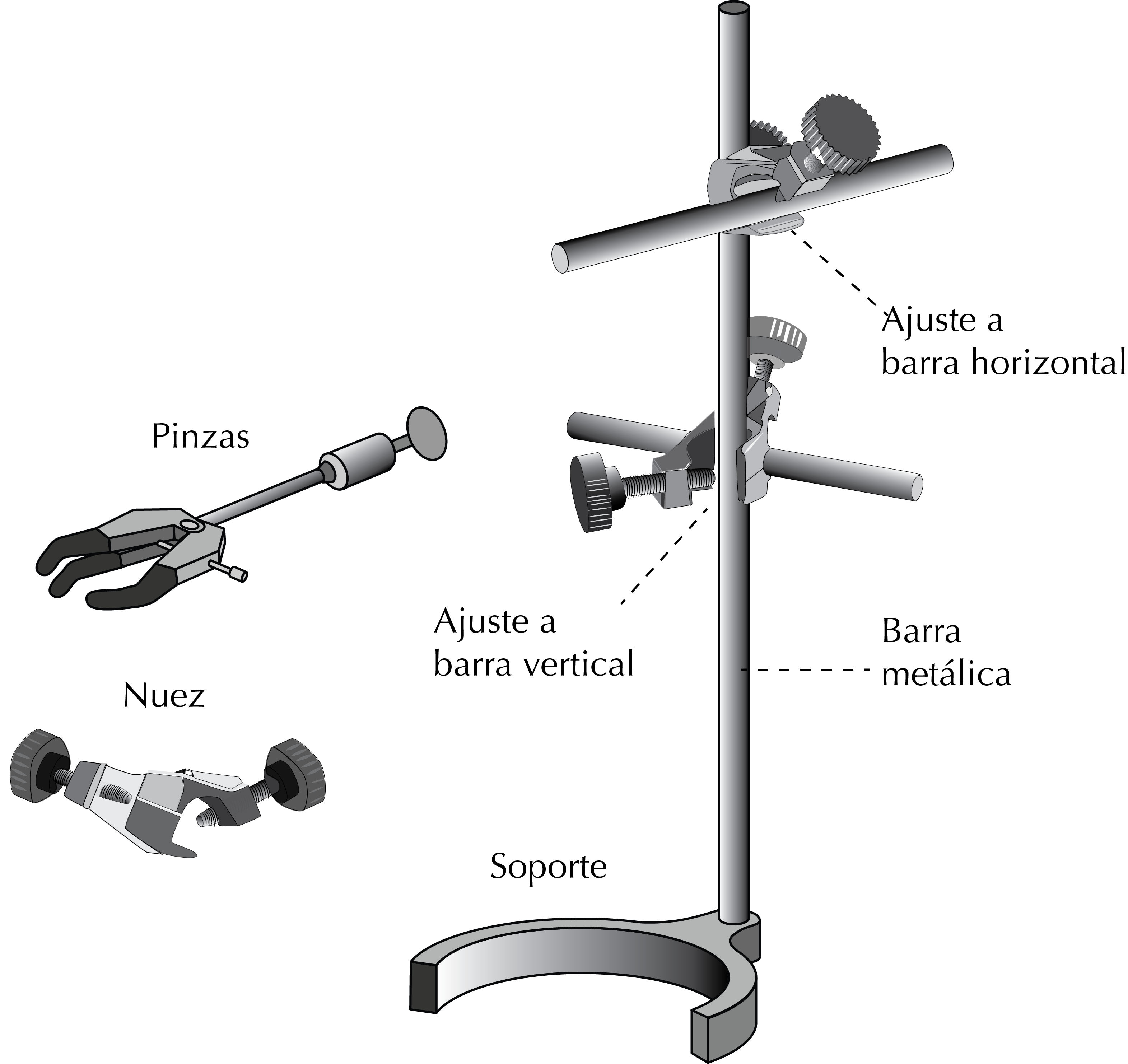

Clamps and holders
These are complementary fastening devices. The clamps can grasp different glassware such as flasks or more complex as- semblies. They consist of a metal rod and two moving metal parts lined with plastic or rubber for easy grip on the glass. Three-finger clamp grips close on themselves by turning a screw, holding the glass without over- tightening and thus avoiding glass breakage.
The clamp is attached to a support by a holder, which is a metal piece with two screws fastening the clamp to the metal rod. There are also clamps that carry a holder built into the structure. Ground-glass flasks have a flange. The clamp must be fixed under this flange to ensure adequate attaching.
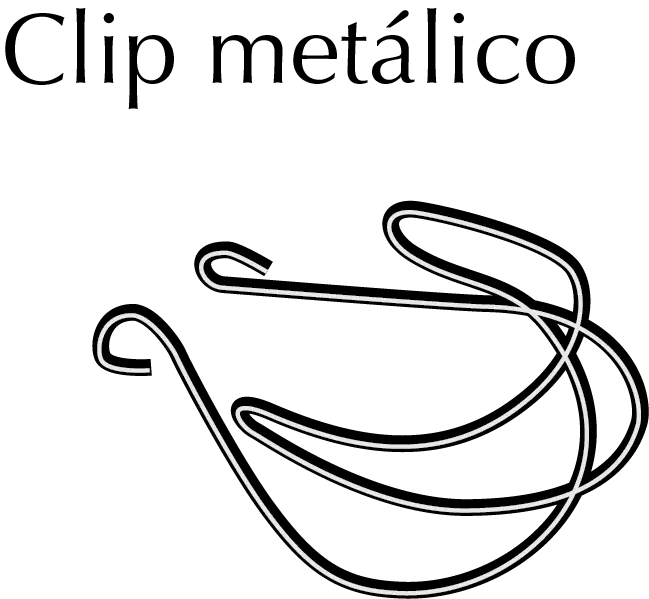
Conical joint clips
These are removable metal clips used for tapered ground joints, manufactured of stainless steel and used especially in com- plex assemblies. There are different clip types depending on the standard size taper.

Keck clips
Keck clips (patented in 1984 by Hermann Keck) are used to hold together the conical ground-glass pieces. These clamps are joint size color coded with standard tapers of red size 29, green size 24, and yellow size 14. Made of polyacetal (polyoxymethylene POM), they melt at 175 ºC and soften at 140 ºC. Therefore, these should not be used to join pieces that can reach these temperatures such as in heating under reflux.

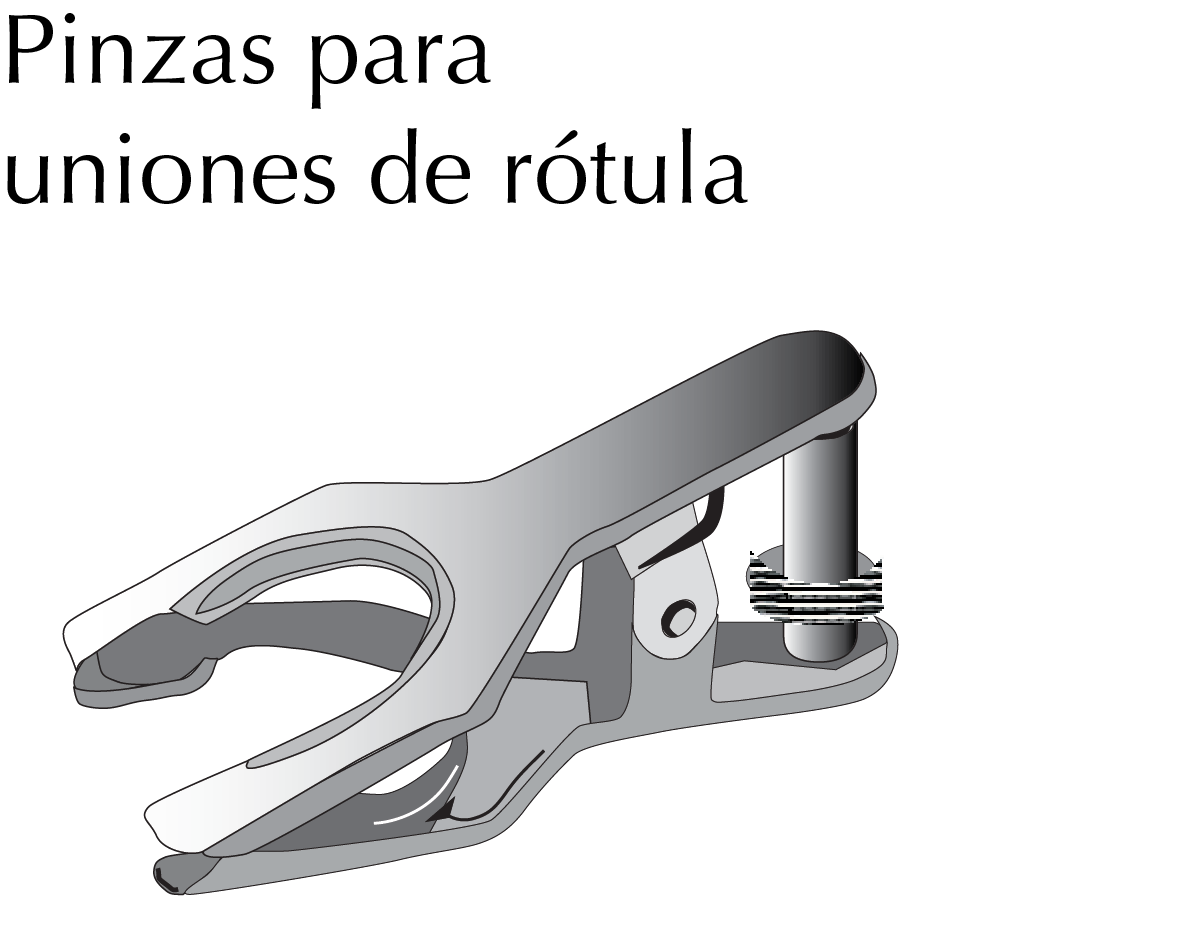
Metal ball joint clip
They are a kind of clamp is used to hold spherical glass ball-and-socket joints. It is commonly used in the rotary evaporators for the clamping of the receiving flask.

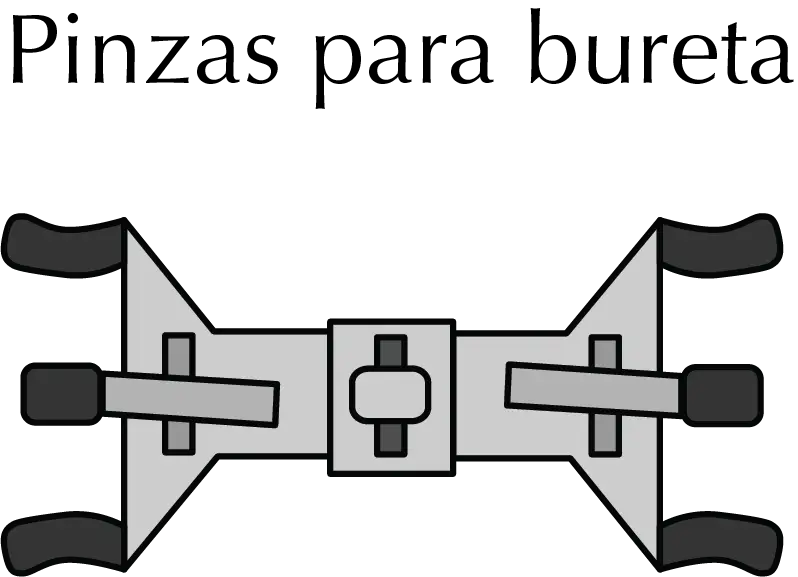
Burette clamps
Burette clamps (also called double “Fisher”-type clamps) were designed to hold a specific burette, with double locking at two nearby points, which prevent the burette from turning (usually when subjected to lab clamp and holder). They also have a very simple system that exerts just enough pressure to secure it firmly while avoiding overpressure that could break glass (as in the case of a three-finger clamp).
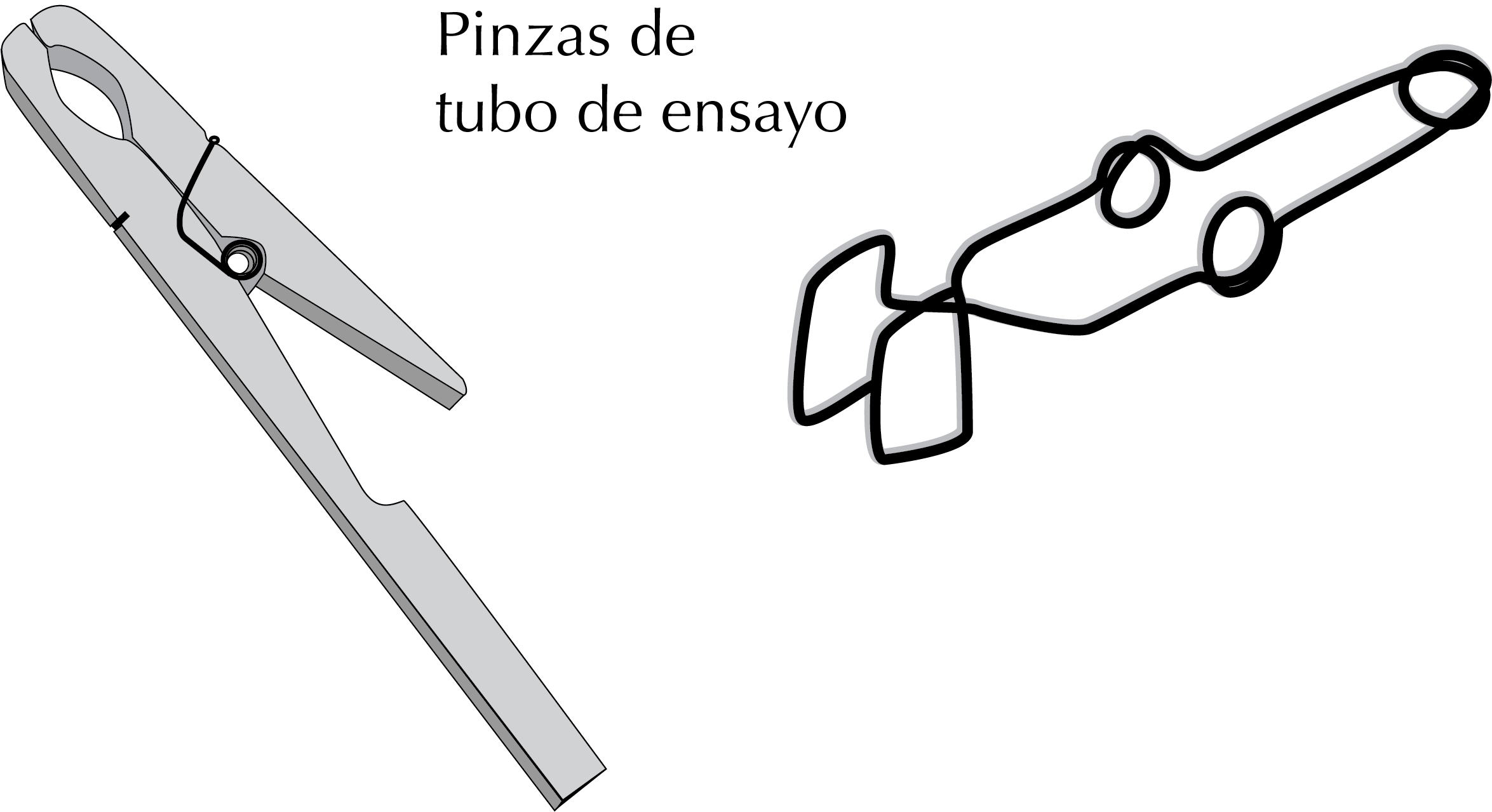
Test tube clamps/tongs
These clamps, used to hold test tubes while being heated or handled, are mainly of two types: wood, similar to clothespins, but with one elongated end, and metal, which are more resistant wear and durable. However, unlike wood, metal is conductive and, if overheated, burns the fingers.
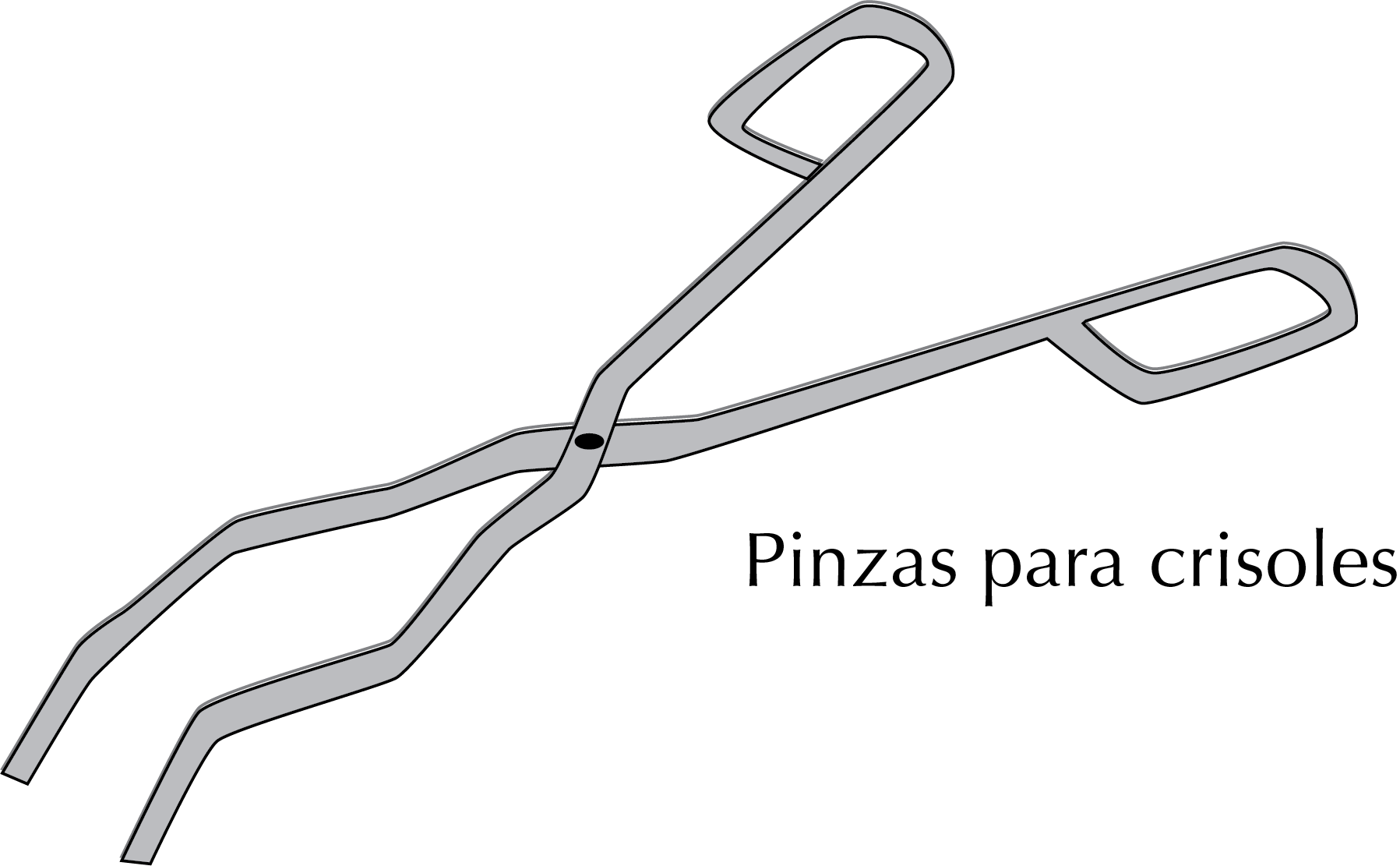
Crucible tongs
Used to handle crucibles, these are made of metal and also require appropriate gloves when used for this purpose. They are also used to handle the oven-dried material, instead of using a cloth or bare hands.
Beaker clamps
Similar to the crucible tongs, but of a larger size, they differ from these in that the jaws of the clamp have a special padding silicone that protects the containers and serves as a thermal insulator. Used for safe and easy operation of vessels, and various other containers when they are hot.
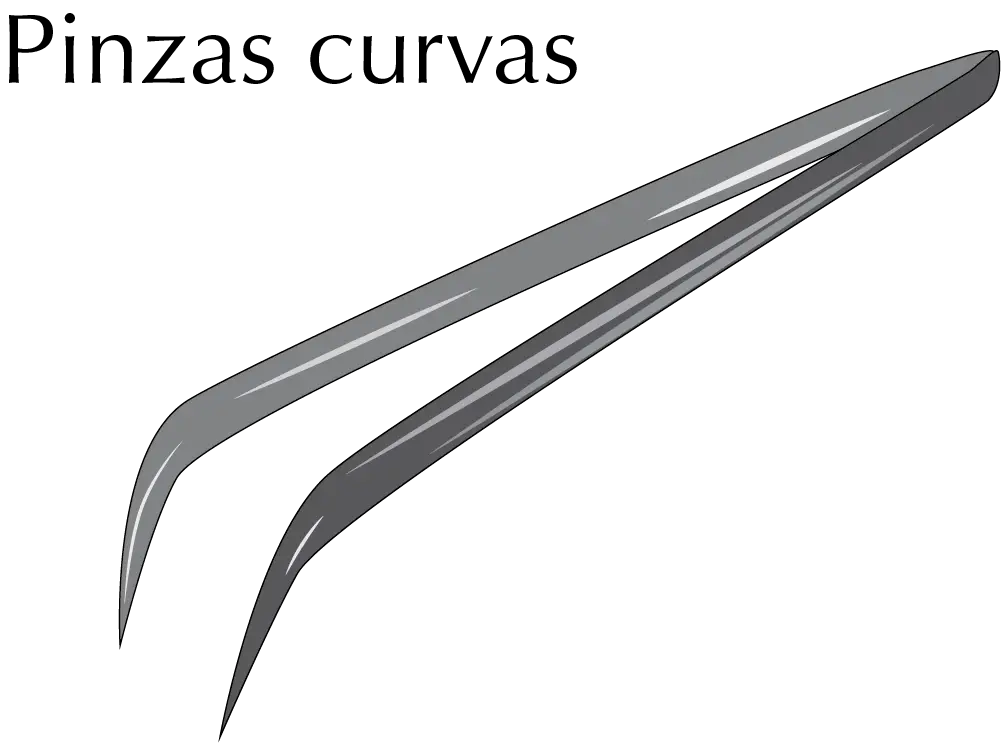
Tweezers/forceps
These are used to hold small items or any solid materials and are useful, for example, when preparing a drying tube (guard tube) to manipulate wool inside. There are models on the market with curved tips that facilitate access to holes and are made of stainless steel or plastic.

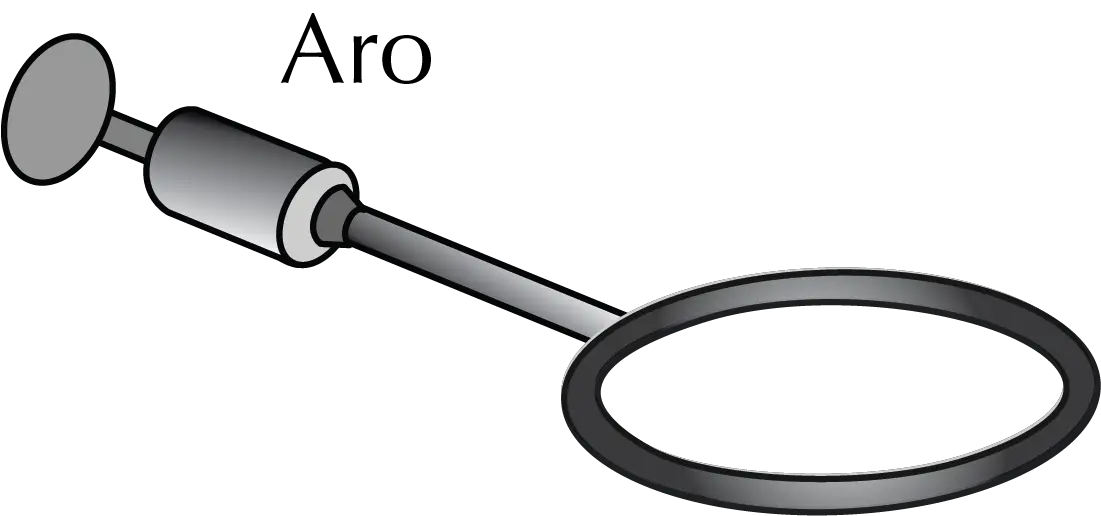
Ring clamps
These devices are used to support funnels such as separatory or filter funnels. In some, the end is coupled to a holder to secure them to the metal support. It is appropriate to protect metal rings with a piece of rubber tubing to avoid damaging the funnels. There are rings that are not completely closed to facilitate placement of the funnels.

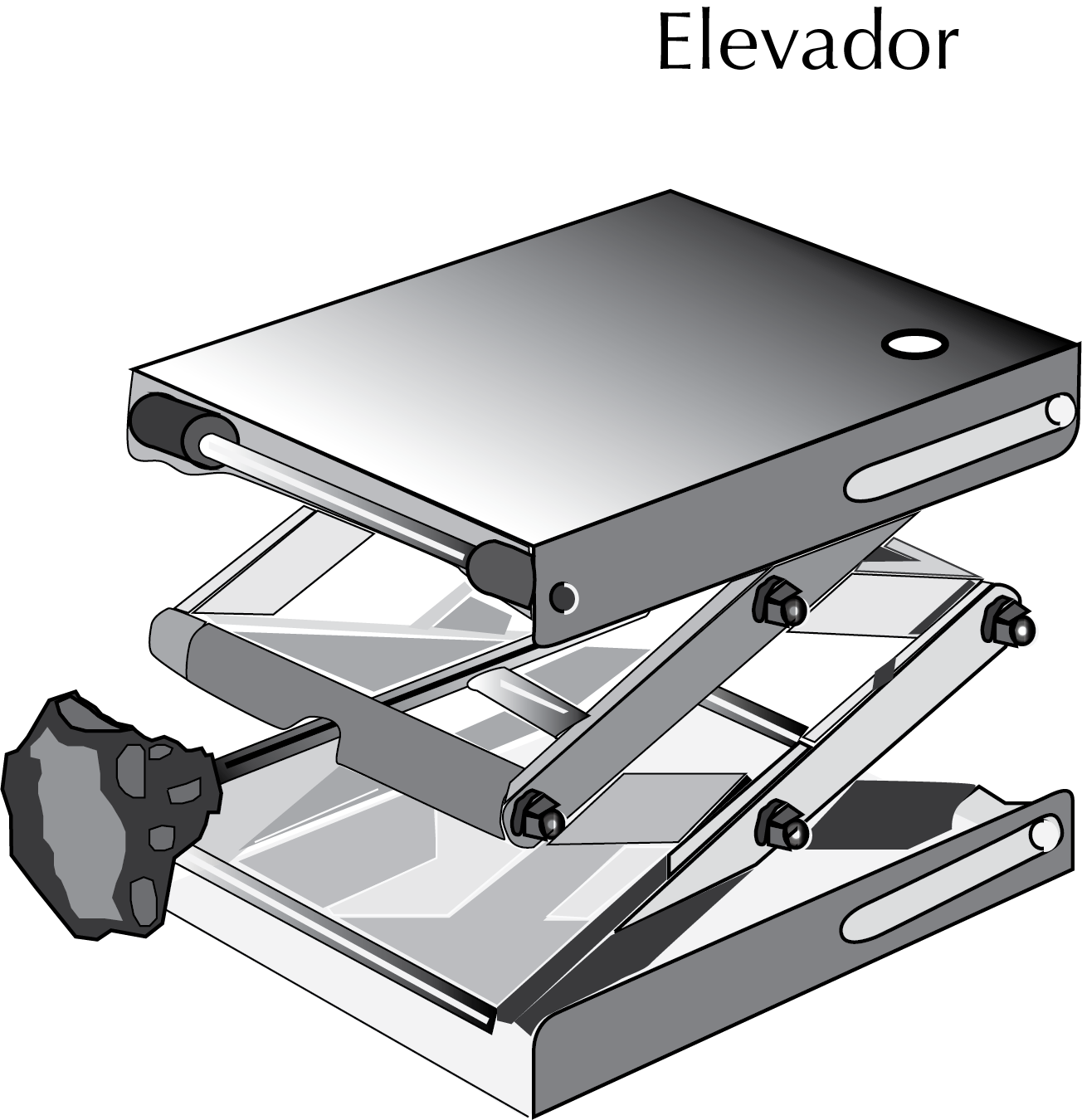
Lab jack
These height-adjustable platforms facilitate the distribution and assembly of laboratory experiments, supporting or elevating lab equipment to appropriate heights. They improve overall lab safety, eliminating the need for clips and for placing glass joints under tension.
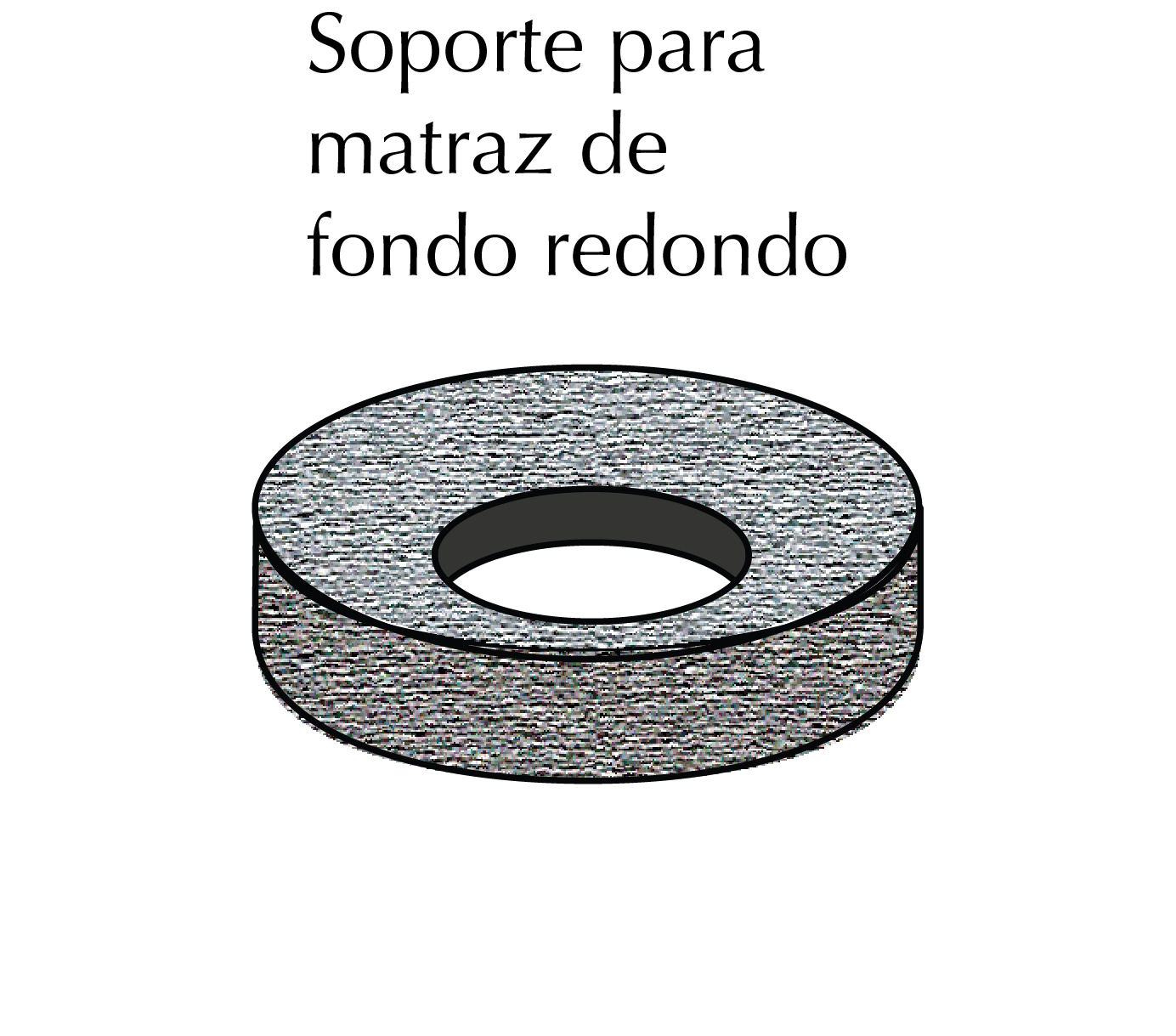
Round-bottom flask stand
For the safe handling, of round-bottom flasks, these stands are manufactured in both cork (cork rings) and plastic (poly- propylene) materials to prevent these containers from rolling on the lab bench.

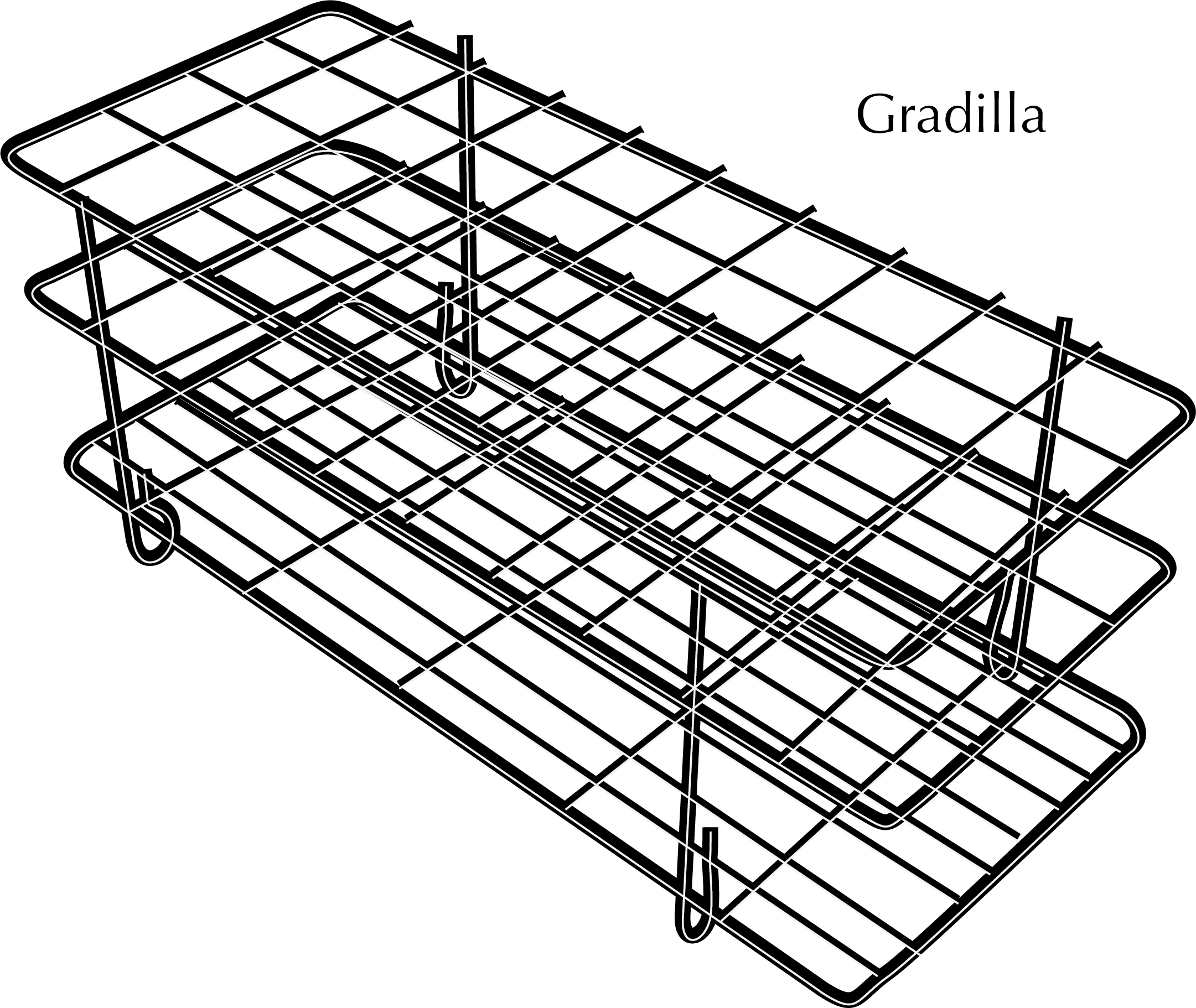
Test-tube rack
These racks are used to hold test tubes, and although traditionally manufactured in wood, today they are manufactured in metal and recently in plastics such as PP, which presents the advantage that the racks can be assembled and put in an autoclave.
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2