What is Buchwald-Hartwig amination?
The Buchwald-Hartwig amination reaction is a method for producing arylamine products. It involves reacting aryl halides with secondary amines in the presence of a silylamide base and tri-o-tolyphopshine palladium complexes. The resulting reaction yields the desired arylamine products.
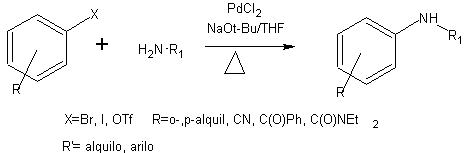
- X = Br, I, OTf
- R = o-alkyl, p-alkyl, CN, C(O)Ph, C(O)NEt2 (see acronyms)
- R’ = alkyl, aryl
References
- J. Louie, J.F. Hartwig, “Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of arylamines from aryl halides. Mechanistic studies lead to coupling in the absence of tin reagents” Tetrahedron Letters 36, 3609-3612 (1995)
- Guram, A.S.; Rennels, R.A.; Buchwald, S.L. “A Simple Catalytic Method for the Conversion of Aryl Bromides to Arylamines“, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1995, 34 (12), 1348-1350.
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.