What is von Richter rearrangement?
The von Richter rearrangement, also known as the von Richter reaction, involves the carboxylation of para– or meta-substituted aromatic nitro compounds with cyanate at temperatures ranging from 120-270 °C.
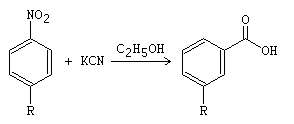
In the von Richter rearrangement, the carboxyl group enters with cine substitution in a position ortho to the eliminated nitro group, resulting in the formation of a new substituted aromatic compound.
References
- v. Richter, V. (1871), Ueber die Einwirkung des Cyankalium’s auf Bromnitrobenzel. [On the effect of cyanide on bromine nitrobenzel.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 4: 21-22. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.18710040111
- v. Richter, V. (1871), Untersuchungen über die Constitution der Benzolderivate. [Studies on the constitution of benzene derivatives.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 4: 459-468. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.187100401154
- v. Richter, V. (1871), Untersuchungen über die Constitution der Benzolderivate. [Studies on the constitution of benzene derivatives.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 4: 553-555. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.18710040208
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.