What is Ladenburg rearrangement?
The Ladenburg rearrangement is a chemical reaction that occurs through thermal rearrangement of an alkyl- or benzylpyridinium halide, leading to the formation of an alkyl- or benzylpyridine.
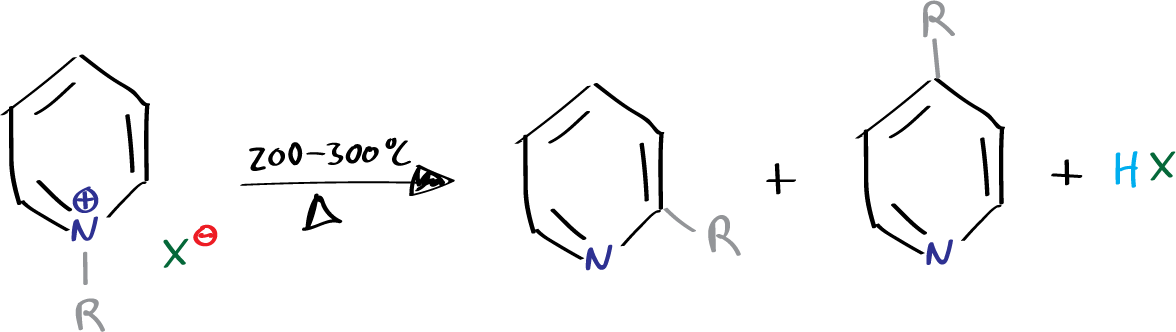
When N-alkyl or benzylpyridinium halides are heated, a rearrangement occurs to form a mixture of ortho– and para-alkylpyridinium halides, which eventually yields the corresponding o– and p-alkylpyridines.
References
- Ladenburg, A. (1883), Methode zur Synthese in der Pyridinreihe. “Method for synthesis in the pyridine series.” Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 16: 1410-1411. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.188301601310
- Ladenburg, A. (1888), Ueber Pyridin- und Piperidinbasen. [On pyridine and piperidine bases.] Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem., 247: 1-98. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.18882470102
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.