Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
The purpose of this experiment is to obtain a carboxylic acid by oxidation of a primary alcohol using hypochlorite as oxidant.
Experimental procedure
An alternative method to the use of carcinogenic chromium(VI) salts for the oxidation of alcohols is the use of a green oxidizing agent such as hypochlorite. One of the most common sources of hypochlorite is bleach, which is actually an aqueous solution of calcium hypochlorite.
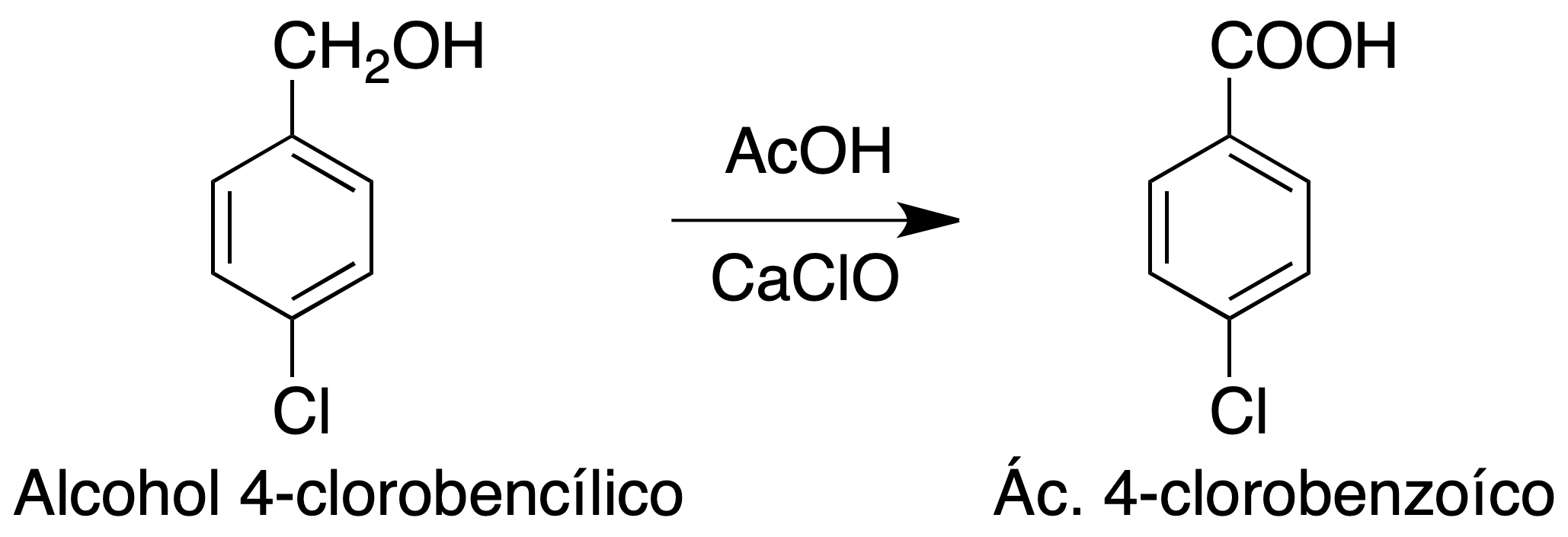
In the case of primary alcohols, oxidation with hypochlorite allows carboxylic acids to be obtained if an excess is used, since the reaction proceeds through an aldehyde which is subsequently oxidized to acid.
Experimental procedure
In an Erlenmeyer dissolve 0.5 g of 4-chlorobenzyl alcohol in 5 ml of acetonitrile. On the other hand, 2.4 g of commercial calcium hypochlorite (65 %) are weighed and transferred to a round bottom flask. They are added 20 ml of water while stirring with a stir bar. Maintaining the agitation 2 ml of glacial acetic acid is added, drop by drop. The reflux condenser is coupled and the set is introduced in a water bath.
With the aid of a Pasteur pipette the alcohol solution is added through the condenser. Once the addition is finished, the reaction is heated, during 1 h, to bain-marie shaking vigorously, and avoiding that the temperature of the bath exceeds the 50 ºC. Subsequently, it is cooled down to room temperature.
The reaction crude is transferred into a separating funnel, 10 ml water is added and the flask is washed with 10 ml diethyl ether and poured over the separatory funnel and extracted. Then it is extracted again with diethyl ether (2 x 10 ml). The ether extracts are pooled and treated with two 10 ml portions of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution.
The aqueous phases are brought together and acidified with 5 % HCl up to pH = 3, obtaining a precipitate (4-chlorobenzoic acid) which is separated by filtration under vacuum. The product is recrystallized from MeOH.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetic acid | 60.05 | 16.2 | 118 | 1.049 |
| Acetonitrile | 41.05 | -48 | 81-82 | - |
| Calcium hypochlorite | 142.98 | 100 | - | 2.350 |
| Diethyl ether | 74.12 | -116 | 34.6 | 0.71 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| MeOH | 32.04 | -98 | 64.7 | 0.791 |
| p-Chlorobenzoic acid | 156.57 | 238-241 | - | - |
| 4-Chlorobenzyl alcohol | 142.58 | 68-71 | 234 | 1.200 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetic acid |   |
| Acetonitrile |   |
| Calcium hypochlorite |     |
| Diethyl ether |   |
| HCl |   |
| MeOH |    |
| p-Chlorobenzoic acid |  |
| 4-Chlorobenzyl alcohol | Non-hazardous |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetic acid | QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetonitrile | WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Calcium hypochlorite | ZKQDCIXGCQPQNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Diethyl ether | RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MeOH | OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Chlorobenzoic acid | XRHGYUZYPHTUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 4-Chlorobenzyl alcohol | PTHGDVCPCZKZKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145