Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on November 12, 2024
Objective of Aspirin Synthesis: Purpose and Application
The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the students with the reaction of esterification getting aspirin (acetyl salicylic acid) from the salicylic acid and acetic anhydride.
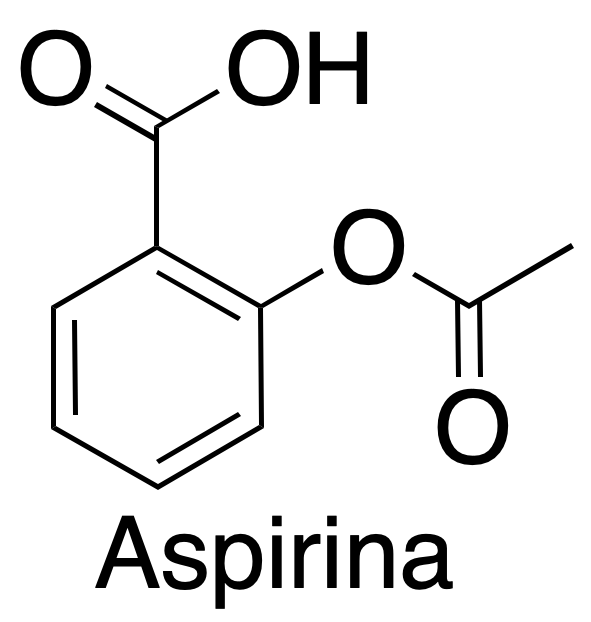 |
| 3D structure |
Historical and Scientific Background of Aspirin Synthesis
Acetylsalicylic acid is marketed under the name of aspirin for the home Bayer being one of the drugs most consumed in the world. It was synthesized at the end of the last century by the German chemist Felix Hofmann.
It uses a reaction of esterification catalyzed acid (H2SO4 or H3PO4 ), where the salicylic acid treated with acetic anhydride gives acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). In this reaction, it becomes a hydroxyl group to an ester, obtained as a by-product acetic acid.
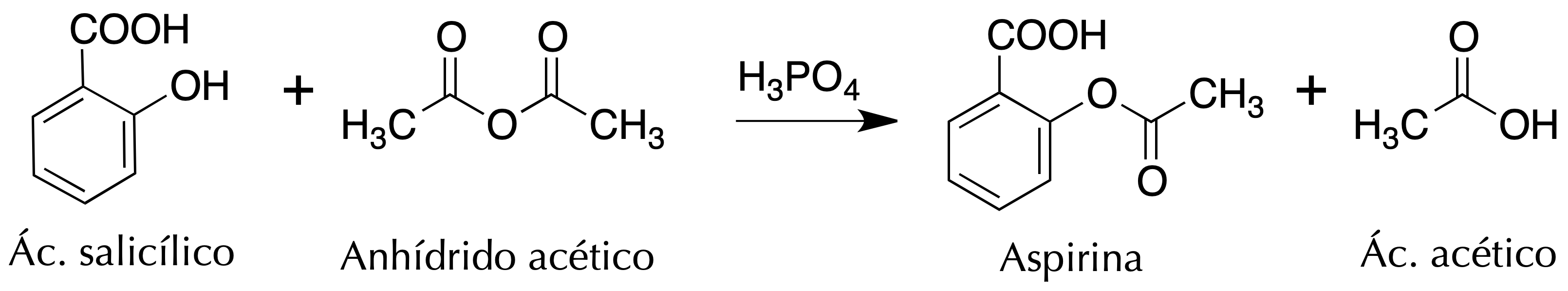
It is a drug that is found in the list of essential medicines of the WHO. Acts as antipyretic, and mainly as an analgesic. As antipyretic exerts its effect on two levels: it increases the heat dissipation by vaso-dilation (action not significant), and acts on the thermostat hypothalamic, which is the central regulator of the body’s temperature.
Their administration route is oral, as it is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The acetylsalicylic acid may be partially hydrolyzed; this, in addition to noticed easily by the smell of acetic acid, it can be recognized by a trial with FeCl3 and seeing if it produces violet colour.
Reaction Mechanism in Aspirin Synthesis: Step-by-Step
The reaction is catalyzed by acid (phosphoric acid, H3PO4). In a first step occurs the protonation of acetic anhydride as shown in the figure.
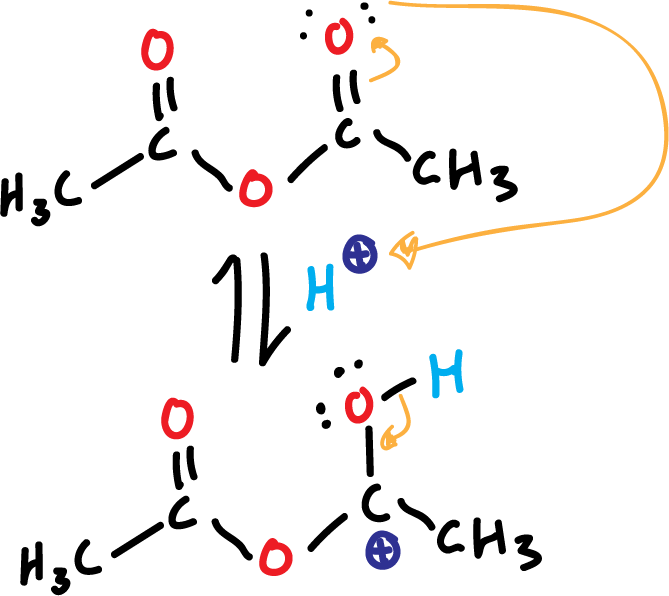
This is going to promote the reactivity of acetic anhydride, which is positively charged at one of the carbons. It is a reaction of esterification of phenol involves the breaking of a link O–H, and is carried out with acetic anhydride.
In a second step, there is an addition: the electron pair of the phenol attacks the carbon positively charged acetic anhydride.
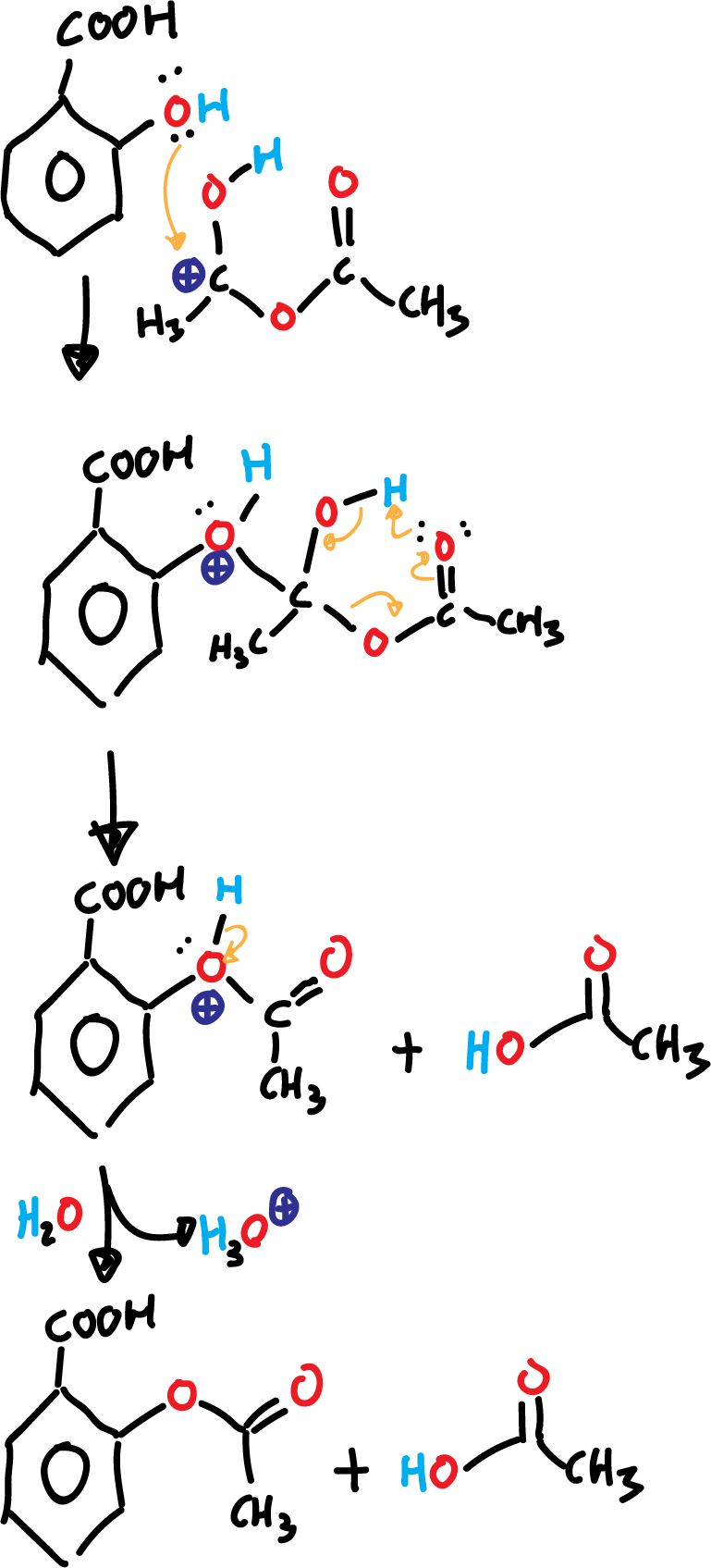
In a third step happens a removal: producing acetic acid and acetyl salicylic acid protonated. The fourth and last step it is a deprotonation by the effect of the water that is added at the end of the reaction.
Experimental Procedure for Aspirin Synthesis in the Laboratory
Place 3 g (0.022 mol) of salicylic acid in a flask of 100 ml. Then, add 6 ml of acetic anhydride and then 6 to 8 drops of phosphoric acid (H3PO4) of 85 %. Subsequently, stir gently to mix the layers and dipped the flask connected to a reflux equipment in a bath of hot water (70-80 °C) for 15 min.
| DANGER! “The acetic anhydride reacts violently with water and the mixture may splatter.” |
Moves the flask from the bath and, while still hot, is added drop by drop to about 1 ml of water, stirring after each addition. Once you have added the first ml of water, can already added quickly, another 20 ml of the same.
The flask is cooled in an ice bath, with what the product should begin to crystallize. Vacuum filter and calculate the performance of the dry product (performance estimated 70 % and melting point 134-136 ° C).
Physico-Chemical Properties of Aspirin: Key Characteristics
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetic acid | 60.05 | 16.2 | 118 | 1.049 |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | 180.16 | 134-136 | - | - |
| H3PO4 | 98.00 | 40 | 158 | 1.685 |
| Acetic anhydride | 102.09 | -73.1 | 139.8 | 1.080 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetic acid |   |
| Acetylsalicylic acid |  |
| H3PO4 |  |
| Acetic anhydride |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetic acid | QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | BSYNRYMUTXBXSQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H3PO4 | NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetic anhydride | WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- D. B. Brown and L. B. Friedman, The Aspirin Project. Laboratory Experiments for Introductory Chemistry, Journal of Chemical Education 50 (1973), no. 3, 214, DOI 10.1021/ed050p214