Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
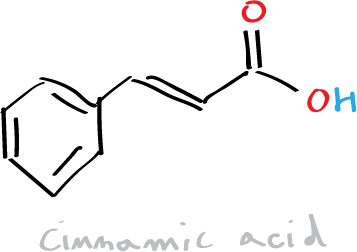
The objective of this experiment is the realization of a condensation between an acid anhydride (acetic anhydride) and an aromatic aldehyde (benzaldehyde) (Perkin reaction or Perkin condensation) in order to synthesize cinnamic acid.
 | |
 |
Background
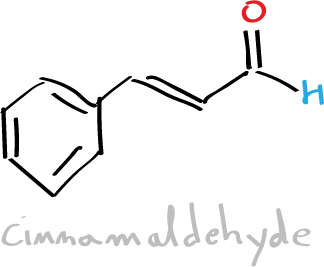
Cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde are natural constituents of cinnamon oil. In this practical, we will proceed to the synthesis of cinnamic acid by means of the Perkin condensation reaction which consists of the reaction between an acid anhydride (acetic anhydride) and an aromatic aldehyde (benzaldehyde) catalyzed by a carboxylate ion.
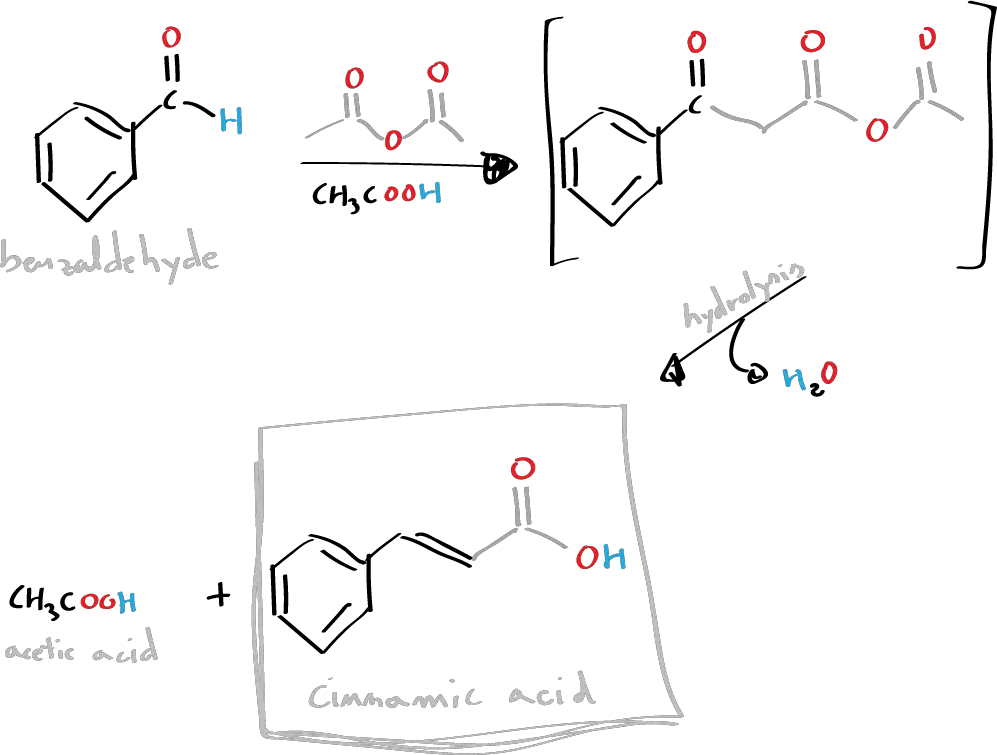
The anhydride generates a carbanion due to the influence of the carboxylate ion, which attacks the carbonyl group of the aldehyde. This is followed by a process of dehydration and hydrolysis of the anhydride functional group.
Experimental procedure
In a 250 ml round bottom flask, fitted with reflux condenser and drying tube, 5 g of benzaldehyde, 7.5 g of acetic anhydride and 2.5 g of anhydrous sodium acetate are placed and heated at reflux for 3 h. It is allowed to cool down to room temperature.
To the cold reaction crude and 100 ml of water are added. Subsequently, a steam distillation (internal steam source) is carried out until all unreacted benzaldehyde (approx. 75 ml distillate volume) is separated and discarded.
The remaining residue is vacuum filtered to remove any resinous solids that have formed. The mother liquor is acidified by slowly adding concentrated HCl. It is cooled in an ice bath and the resulting solid is isolated by vacuum filtration. It is recrystallized from water, dried, weighed and the yield is determined. Estimated yield 60 %.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetic acid | 60.05 | 16.2 | 118 | 1.049 |
| Acetic anhydride | 102.09 | -73.1 | 139.8 | 1.080 |
| Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | -26 | 178-179 | 1.044 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 132.16 | -7.5 | 248 | 1.050 |
| Cinnamic acid | 148.16 | 132-135 | 300 | 1.248 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| Sodium acetate | 82.03 | 328 | - | 1.528 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetic acid |   |
| Acetic anhydride |    |
| Benzaldehyde |  |
| Cinnamaldehyde |  |
| Cinnamic acid |  |
| HCl |   |
| Sodium acetate | Non-hazardous |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetic acid | QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetic anhydride | WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Benzaldehyde | HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Cinnamaldehyde | KJPRLNWUNMBNBZ-QPJJXVBHSA-N |
| Cinnamic acid | WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Sodium acetate | VMHLLURERBWHNL-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- R. E. Buckles, The use of the Perkin reaction in organic laboratory classes, Journal of Chemical Education 27 (1950), no. 4, 210–211, DOI: 10.1021/ed027p210