Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
What is ammonia?
Ammonia is a gas of molecular formula NH3 with a molecular weight (17 g/mol). It has a density under normal conditions of 0.7714 g/L. It has a melting point (pf = -77.8 ºC) and a boiling point (bp = -33.4 ºC). It is very soluble in water (at 0 ºC one volume of NH3 mixes with 1176 volumes of H2O).
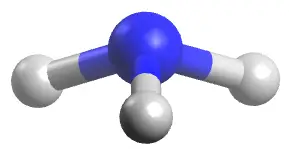 |
| 3D Structure |
It is a colorless gas that has a pungent odor, and in the presence of pure oxygen reacts (burns) to give nitrogen gas and water in the subsequent combustion reaction:
4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O
Gaseous ammonia is irritating to eyes and respiratory tract. When mixed with air in a proportion between 16-27 %, it results in an explosive combination at a temperature of 780 ºC. It is the main precursor of synthetic nitrogen compounds. For example, nitric acid is obtained by the Ostwald method when ammonia burns with oxygen in the presence of a platinum catalyst:
NH3 + 2O2 –(cat. platino)→ 2H2O + HNO3
At elevated temperatures, it readily decomposes to give nitrogen and hydrogen gas:
2NH3 → 2N2 + 3H2
Ammonia is obtained by Haber process and is mainly used in the preparation of ammonium sulfate and also in the preparation of Solvay process (soda process).