Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
How are alcohols named?
The IUPAC allows several nomenclature systems for the alcohols listed below:
- Substitutive nomenclature: it is named with the prefix indicating the number of carbons followed by the termination –ol (recommendation C-201.1). To place the function in a chain, the lowest locator is used.
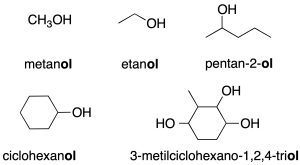
- Radical-function nomenclature (only applicable to simple alcohols): this consists of first citing the name of the function (alcohol) and then the name of the radical as if it were an adjective (recommendation C-201.3).
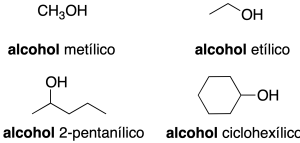
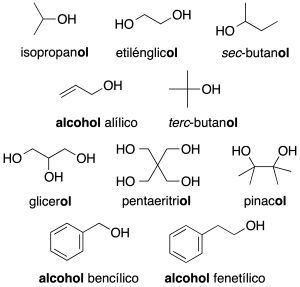
In complex molecules only the first nomenclature system is used. When acting as a substituent: the prefix hydroxy is used (recommendation C-201.3). Alcohols with two neighboring hydroxyl groups are given the generic name glycols. Some common names are retained (recommendation C-201.4).
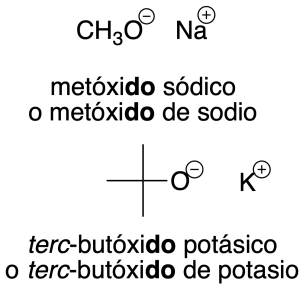
- Radicals derived from alcohols: radicals derived from alcohols of the R-O- type are named by adding the ending –oxy to the name of the radical (recommendation C-205.1). For simpler radicals, abbreviations are often used and are indicated in the figure in parentheses.
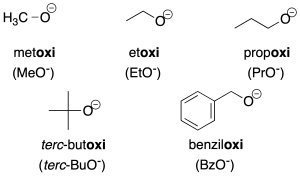
Salts derived from these radicals are assigned the same name as the radical ending in –de followed by the name of the cation (recommendations C-206.1 and C-206.2).
Nomenclature of Phenols
Generically, they are arenes that have at least one -OH group. The first term in the series is phenol, with an -OH attached to benzene, which gives this family of compounds its name.
The OH group in an aromatic ring does not have a high priority. Therefore it is found as the main group (-ol) but more often as a secondary one (-hydroxy-).
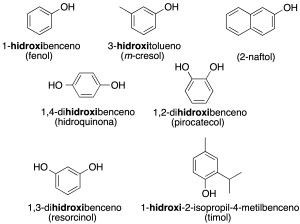
They are named like the corresponding alcohols, with the ending –ol added to the name of the hydrocarbon. However, the prefix hydroxy– can also be used together with the name of the hydrocarbon (recommendation C-202.1).
Some of these compounds retain common or trivial names (indicated here in parentheses) (recommendation C-202.2).
The corresponding Ar-O-type radicals are named similarly to the alcohol derivatives (recommendation C-205.1).
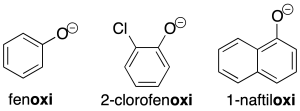
The salts derived from these radicals are named analogously to the corresponding salts of the alcohols.