What is Hayashi rearrangement?
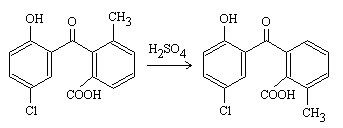
The Hayashi rearrangement is a chemical reaction that occurs when o-benzoylbenzoic acids are exposed to either sulfuric acid or phosphorous pentoxide. During this reaction, the molecular structure of the substrate undergoes a rearrangement, resulting in the formation of a new product.
References
- M. Hayashi, “CCCXXXVI.—A new isomerism of halogenohydroxybenzoyltoluic acids” J. Chem. Soc., 1927, 2516-2527
DOI: 10.1039/JR9270002516 - M. Hayashi, “CXCII.—A new isomerism of halogenohydroxybenzoyltoluic acids. Part II. 2-(5′-Chloro-2′-hydroxybenzoyl)-5(4?)-methylbenzoic acid” J. Chem. Soc., 1930, 1513-1519
DOI: 10.1039/JR9300001513 - M. Hayashi, “CXCIII.—A new isomerism of halogenohydroxybenzoyltoluic acids. Part III. 2-(3′-Chloro-4′-hydroxybenzoyl)-3(or 6)-methylbenzoic acid” J. Chem. Soc., 1930, 1520-1523
DOI: 10.1039/JR9300001520 - M. Hayashi, “CXCIV.—A new isomerism of halogenohydroxybenzoyltoluic acids. Part IV. 2-(4′-Chloro-2′-hydroxybenzoyl)-3(or 6)-methylbenzoic acid and 2-(2′-chloro-4′-hydroxybenzoyl)-3(or 6)-methylbenzoic acid” J. Chem. Soc., 1930, 1524-1528
DOI: 10.1039/JR9300001524
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.