What is Rosenmund-von Braun reaction
The Rosenmund-von Braun reaction, also known as the Rosenmund-von Braun synthesis, involves the transformation of aryl halides into aromatic nitriles using cuprous cyanide, CuCN as a catalyst.
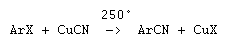
References
- Rosenmund, K.W. and Struck, E. (1919), Das am Ringkohlenstoff gebundene Halogen und sein Ersatz durch andere Substituenten. I. Mitteilung: Ersatz des Halogens durch die Carboxylgruppe. [The halogen bonded to the ring carbon and its replacement by other substituents. I. Communication: Replacement of the halogen by the carboxyl group.] Ber. dtsch. Chem. Ges. A/B, 52: 1749-1756. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.19190520840
- v. Braun, J. and Manz, G. (1931), Fluoranthen und seine Derivate. III. Mitteilung. [Fluoranthene and its derivatives. III. communication.] Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem., 488: 111-126. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.19314880107
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.