What is biotin?
Biotin (vitamin B7, vitamin H, or coenzyme R), is a member of the B vitamin family. It is an enzyme cofactor present in small amounts in every living cell. The IUPAC systematic name is 5-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]pentanoic acid
Chemical structure
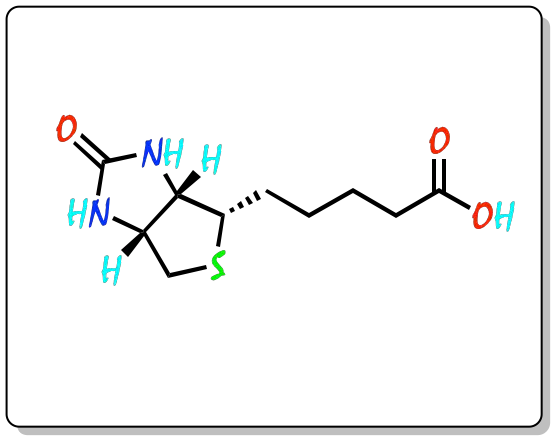 |
| 3D Structure |
Functions
Its main functions in the body are to help with the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins, and in cell growth, facilitating the utilization of the other B vitamins. Biotin also regulates blood sugar levels in people with insulin-dependent or non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
Chemical properties
Food sources
Soybeans, whole grains, egg yolk, almonds, walnuts, oats, mushrooms, broccoli, bananas, peanuts, liver, kidney, milk, legumes, sunflower seeds and nutritional yeast.