Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
What is niacin?
The generic term niacin or vitamin PP refers to nicotinic acid and its amide niacinamide, which are the two main forms of vitamin B3. A third form of niacin, inositol hexaniacinate, is gaining acceptance as a substitute for niacin. This is composed of one molecule of inositol (an “unofficial” B vitamin) and six molecules of niacin.
The systematic name of the IUPAC is pyridin-3-carboxylic acid.
Chemical structure
It has the general formula C6NH5O2. It consists of a pyridine ring substituted with a carboxyl group in position 3.
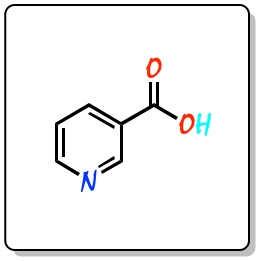 |
| 3D Structure |
Functions
Both niacin and niacinamide are key to releasing energy from carbohydrates, processing alcohol, forming fats and producing sex hormones. A significant benefit of niacin is its ability to prevent recurrent heart attacks. Niacin also helps regulate cholesterol levels.
Chemical properties
Biosynthesis
Niacin is produced in the liver from the amino acid tryptophan by a rearrangement reaction of the 5-membered aromatic heterocycle of tryptophan with an alpha-positioned amino group to form the 6-membered pyridine ring of niacin. This biosynthesis is inefficient and the niacin and niacinamide molecules are absorbed in the diet to generate NAD and NADP, active forms of the vitamin which are stored in the liver and erythrocytes.
Food sources
Peanuts, brewer’s yeast, fish and whole grains.