What is Allan-Robinson reaction?
The synthesis of flavones or isoflavones derivatives through the condensation between o-hydroxyaryl ketones and an anhydride of aromatic acid was first reported by Allan and Robinson (Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1947) in 1924.
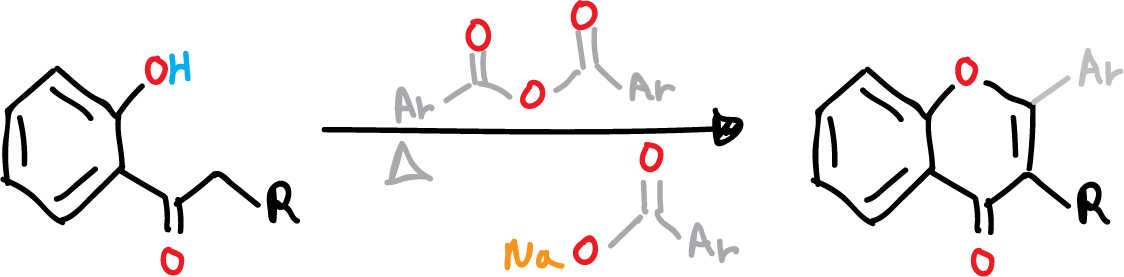
As a result, the Allan-Robinson reaction is commonly referred to as the Allan-Robinson condensation, Allan-Robinson’s flavone synthesis, or Allan-Robinson synthesis.
The application of the Allan-Robinson reaction has been demonstrated in the synthesis of flavonoids and isoflavones, which exhibit diverse structural characteristics.
References
Allan, J., and Robinson, R. (1924). CCXC.—An accessible derivative of chromonol. J. Chem. Soc. Trans., 125(0), 2192-2195. DOI: 10.1039/CT9242502192
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.