Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
To prepare adipic acid from cyclohexene by oxidation with H2O2 and sodium tungstate Na2WO4 using a sustainable alternative to the traditional method using potassium permanganate K2MnO4.
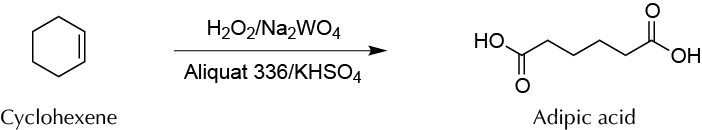
Background
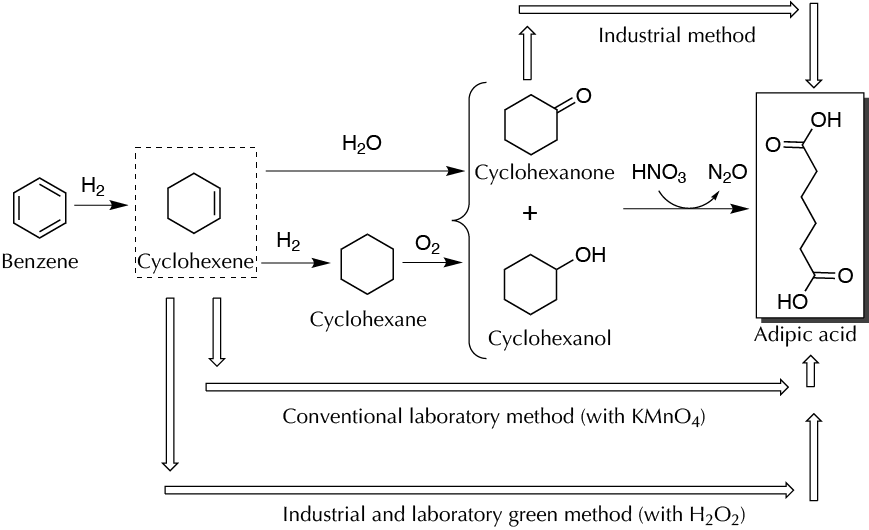
Adipic acid is a substance used for the preparation of nylon, polyurethanes, and other products of commercial interest. The industrial synthesis of adipic acid uses nitric acid oxidation of a mixture of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol termed “KA oil” (ketone and alcohol-oil). This procedure generates nitrous oxide, a substance that increases greenhouse gases, damages the ozone layer, and causes acid rain. On a laboratory scale, it has been traditionally prepared from cyclohexene by oxidation with potassium permanganate. An alternative with less environmental impact than the traditional method involves the preparation of adipic acid from cyclohexene oxidation with H2O2 and sodium tungstate. This procedure is considered a green method and involves a series of events that make a low environmental impact:
- The H2O2 is a green oxidant easy to handle and produces only water as a byproduct of the reaction.
- The sodium tungstate is used in catalytic amounts, is of low toxicity, and can be used several times (recyclable).
- This method is industrially applicable in laboratory scale experiments both at miniscale and microscale.
Experimental procedure
To a 50 ml round-bottom flask, add 0.5 g of tricaprimethyl ammonium chloride (Aliquat-336®), 0.5 g of sodium tungstate dihydrate (Na2WO4 · 2H2O), 11.98 g of H2O2 30 %, and 0.37 g of potassium hydrogen sulfate (KHSO4). Stir the mixture at r.t. using magnetic stirring for 2 min. Then add 2 g of cyclohexene, attach the flask to a water condenser and a drying tube to minimize odors released by the reaction crude. Keep the reaction mixture at reflux for 2 h.
| DANGER! “Gloves should be used due to both the toxicity of Aliquat-336® and because H2O2 can cause burns on contact with skin. In addition, potassium bisulfate is acidic and must be handled with caution.” |
The reaction progress can be monitored (visually) stopping the agitation. At first, the formation of two layers is observed. When transforming cyclohexene to adipic acid, which is soluble in water, the reaction crude will be transformed to present a majority aqueous phase and an oily rest for the phase-transfer catalyst. Furthermore, the phase-transfer catalyst remaining in the round-bottom flask and the tungsten catalyst of the mother liquor from the crystallization of succinic acid can be recycled.
Once reflux has been completed, while still hot, transfer only the aqueous layer (with a Pasteur pipette) to an Erlenmeyer to avoid coprecipitation of Aliquat-336®. Adipic acid appears as a precipitate on cooling the aqueous layer. Filter the solid produced under vacuum, wash with 5 ml of cold water, and purify by recrystallization from water. Once dried, weigh and calculate the yield (approximately 70 %).
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Adipic acid | 146.14 | 151-154 | 337.5 | 1.36 |
| Aliquat® 336 | - | -6 | - | - |
| Cyclohexene | 82.14 | -104 | 83 | 0.779 |
| H2O2 | 34.01 | - | - | 1.110 |
| KHSO4 | 136.17 | 214 | - | 2.320 |
| Na2WO4·2H2O | 329.85 | 698 | - | 4.180 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Adipic acid |  |
| Aliquat® 336 |    |
| Cyclohexene |    |
| H2O2 |   |
| KHSO4 |   |
| Na2WO4·2H2O |  |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Adipic acid | WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Aliquat® 336 | |
| Cyclohexene | HGCIXCUEYOPUTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H2O2 | MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| KHSO4 | CHKVPAROMQMJNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Na2WO4·2H2O | WPZFLQRLSGVIAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |