Objective
To synthesize α-glycol (pinacol) from ketone by radical condensation and to dehydrate α-glycol to form pinacolone.
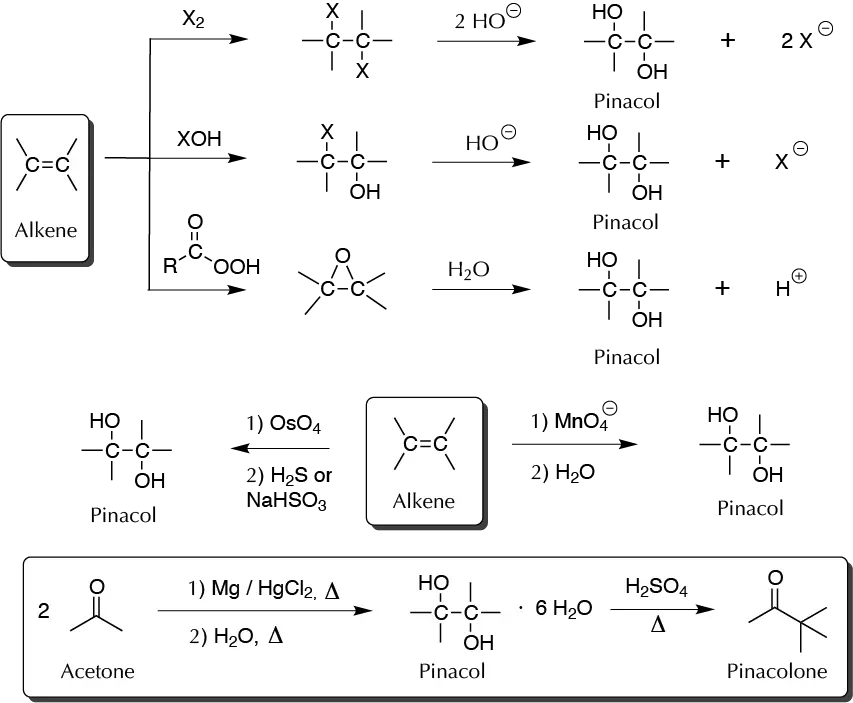
Background
Glycols can be synthesized by numerous methods, and this product can be used as starting olefin or unsaturated carbonyl compounds. For example, from olefins the synthesis can be carried out by adding halogen, by adding hypohalogenous acid (XOH), by epoxidation with peracid and subsequent hydrolysis of the epoxide formed, or by adding OsO4 and/or MnO4– . Moreover, pinacol synthesis is induced by a reductive coupling of acetone. This ketone is treated with an active metal (Na or Mg), resulting in a transfer of an electron to the carbonyl producing a cetyl radical, which dimerizes, leading to C−C bond formation and yielding the diol. With aromatic ketones the synthesis can also be carried out photochemically. Thus, the pinacolinic transposition is formally a dehydration between two molecules ketone catalyzed by an acid medium.
Experimental procedure
A) Preparation of pinacol (2,3-dimethyl-butane-2,3-diol)
In a dry 100 ml round-bottom flask, place 3 g of magnesium and 0.5 g mercuric chloride HgCl2. Add 10 ml of anhydrous acetone and stir until the reaction begins. Adapt the flask with a reflux condenser and gradually add another 40 ml of acetone. Stir for 15 to 20 min, and add another 25 ml of acetone. After 30 to 45 min, heat the mixture in a water bath to maintain a good reflux rate. After 1 h of reflux, end the reaction. Remove the flask and connect the condenser via an adapter to a vacuum line, while continuing to heat the flask, thereby removing the excess acetone (rotary evaporator can alternatively be used), and magnesium pinacolate is as a powder. Reconnect the reflux condenser and add 100 ml of water containing 5 g of trisodium phosphate through the condenser (mildly heating the reaction). Reflux the flask for 15 min. Vacuum filter the hot mixture and cool the filtrate in an ice bath with stirring. A precipitate will appear. When the crystallization is complete, vacuum filter and wash the resulting crystals with 25 ml of ice water or with 25 ml of petroleum ether.
| DANGER! “The mercuric salts are toxic and therefore handle with caution, wearing gloves.” |
B) Preparation of pinacolone (2,3-dimethyl-butan-2-one)
In a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask, place 15 ml of water and add slowly and carefully 10 ml of H2SO4 (conc.). Then add 6 g pinacol previously prepared and dissolved, transfer to a flask, and distill. Allow the distillate to stand and then dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate Na2SO4 and gravity filter.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetone | 58.08 | -94 | 56 | 0.791 |
| H2SO4 | 98.08 | 3 | - | 1.80-1.84 |
| HgCl2 | 271.50 | 277 | 302 | 5.440 |
| Magnesium | 24.31 | 648 | 1,090 | 1.740 |
| Na3PO4 | 163.94 | 75 | - | 1.620 |
| Petroleum ether | - | <-30 | 30-60 | 0.640 |
| Pinacol | 118.17 | 41 | 174 | 0.967 |
| Pinacol hexahydrate | 226.27 | - | - | - |
| Pinacolone | 100.16 | - | 103-107 | 0.850 |
| p-Xylene | 106.17 | 13.0 | 138.4 | 0.860 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetone |   |
| H2SO4 |  |
| HgCl2 |     |
| Magnesium |  |
| Na3PO4 |   |
| Petroleum ether |     |
| Pinacol |   |
| Pinacol hexahydrate | See MSDS |
| Pinacolone |   |
| p-Xylene |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetone | CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H2SO4 | QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HgCl2 | LWJROJCJINYWOX-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Magnesium | FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Na3PO4 | RYFMWSXOAZQYPI-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| Petroleum ether | |
| Pinacol | IVDFJHOHABJVEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Pinacol hexahydrate | LEQNJUZEJVNIIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Pinacolone | PJGSXYOJTGTZAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Xylene | URLKBWYHVLBVBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145