Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
The purpose of this experiment is to study the oxidative cleavage of a double bond.
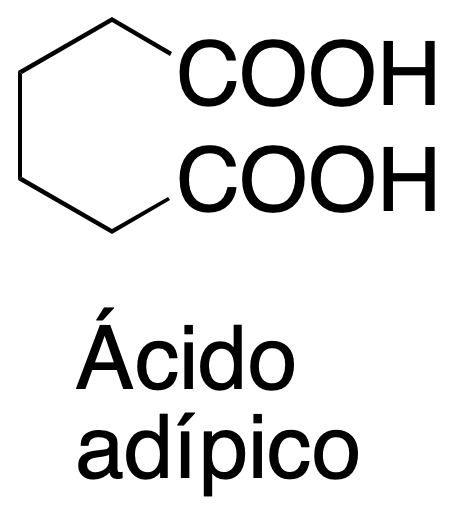
Background
Potassium permanganate, KMnO4, is an oxidant commonly used in organic chemistry. In this practical, it will be used to produce the oxidative cleavage of a double bond to obtain two carboxylic groups at the ends of the bond.

Experimental procedure
A solution of 6.3 g of potassium permanganate in 100 ml of water is prepared in a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask. The permanganate dissolves slowly, so it is necessary to stir until dissolution. Over a period of 10 min, the KMnO4 solution is added (in portions of about 10 ml) to another solution of 1.24 ml (1.24 g) of cyclohexene in 10 ml of acetone contained in a second 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask, with magnetic stirring. After the additions are completed, the mixture is heated to 55-60 °C in a water bath for 30 min. After this time, the Erlenmeyer is removed from the water bath, 1 g of sodium bisulfite, NaHSO3, is added to the dark reaction mixture and cooled in an ice bath.
Filter under vacuum the reaction crude, rinsing the Erlenmeyer with 25 ml of water. Pour the contents over the brown precipitate in the funnel. Transfer the clear filtrate to a 500 ml beaker and acidify with HCl to pH = 2 (check with indicator paper). Evaporate the solution until the filtrate is concentrated to a volume of about 10 ml. Cool this concentrated solution in an ice bath so that a solid will appear, which is then vacuum filtered and the adipic acid precipitate is allowed to dry in an air stream. The product thus obtained (adipic acid) is recrystallized from water, weighed after drying and the yield is calculated (estimated yield 60 %).
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Adipic acid | 146.14 | 151-154 | 337.5 | 1.36 |
| Cyclohexene | 82.14 | -104 | 83 | 0.779 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| KMnO4 | 158.04 | 240 | - | 2.71 |
| NaHSO3 | 104.06 | - | - | 1.48 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Adipic acid |  |
| Cyclohexene |    |
| HCl |   |
| KMnO4 |    |
| NaHSO3 |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Adipic acid | WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Cyclohexene | HGCIXCUEYOPUTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| KMnO4 | VZJVWSHVAAUDKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaHSO3 | DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- K. Sato, M. Aoki, and R. Noyori, A green route to adipic acid: direct oxidation of cyclohexenes with 30 percent hydrogen peroxide, Science 281 (1998), no. 5383, 1646–1647, DOI: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1646
- S. M. Reed and J. E. Hutchison, Green chemistry in the organic teaching laboratory: an environmentally benign synthesis of adipic acid, Journal of Chemical Education 77 (2000), no. 12, 1627, DOI: 10.1021/ed077p1627
Return to the Organic Synthesis Experiments.
Articles on the website