Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
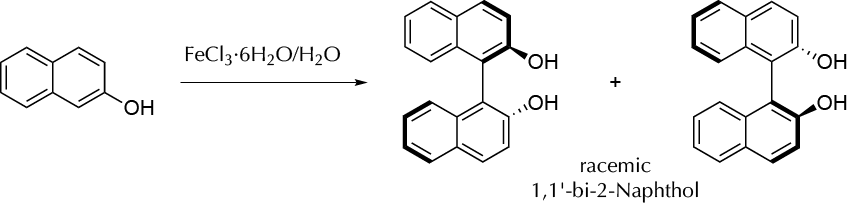
Synthesis of racemic 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol by an oxidative coupling reaction in aqueous media.
Background
1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol is a compound that can be used as a ligand for transition- metal. 1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol is an example of molecule that presents atropisomers. Enantiomeric pure complex of such derivatives can be used as a catalyst in some asymmetric syntheses but may undergo racemization upon heating. Racemic 1,1′-bi-2-naphthol can be prepared using iron(III) salts as an oxidant. The mech- anism involves a process of complexation of iron(III) with the hydroxyl group of 2-naphthol, followed by a radical coupling reaction of the naphthol rings started by iron(III) that is reduced to iron(II). In this case, the reaction is performed in water.
Experimental procedure
To a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask, add a solution of FeCl3·6H2O (11.4 g, 42 mmol) in 40 ml of water and 2-naphthol (3 g, 21 mmol) finely powdered. Heat the Erlenmeyer in a water bath at 50 ºC for 2 h while stirring the mixture with a magnetic stirrer. Cool the resulting green suspension to room temperature and separate the solids by vacuum filtration. Dissolve the solid residue with 50 ml of CH2Cl2 and transfer the solution to a separatory funnel. Extract the organic solution with HCl 1 M (2 × 40 ml) and with water (2 × 40 ml) to remove the inorganic salts. Transfer the organic solution to an appropriate flask, and dry it with anhydrous magnesium sulfate. Remove the desiccant by gravity filtration, in a tared round-bottom flask. Eliminate the solvent under vacuum by rotary evaporator to recover a light-brown solid (1,1′-bi-2-naphthol), which can be purified by recrystallization from a minimum amount of hot toluene (estimated yield 70 %).
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| CH2Cl2 | 84.93 | -97 | 40.0 | 1.33 |
| FeCl3·6H2O | 270.3 | 280-285 | 37 | 1.820 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| MgSO4 | 120.37 | 1124 | - | 1.070 |
| Toluene | 92.14 | -93 | 110.6 | 0.867 |
| β-Naphthol | 144.17 | 120-122 | 285-286 | 1.280 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| CH2Cl2 |  |
| FeCl3·6H2O |   |
| HCl |   |
| MgSO4 | Non-hazardous |
| Toluene |    |
| β-Naphthol |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| CH2Cl2 | YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| FeCl3·6H2O | NQXWGWZJXJUMQB-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MgSO4 | CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Toluene | YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| β-Naphthol | JWAZRIHNYRIHIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- K. K. W. Mak, Synthesis and resolution of the atropisomeric 1,1’-bi-2-naphthol: An ex- periment in organic synthesis and 2-D NMR spectroscopy, Journal of Chemical Education 81 (2004), no. 11, 1636–1640, DOI: 10.1021/ed081p1636