What is Dess-Martin reagent?
The Dess-Martin reagent, also known as Dess-Martin periodinane (DMP), Dess-Martin Periodinane reagent, or Dess-Martin oxidant, which tolerates a variety of functional groups, is a powerful and versatile oxidizing agent that is widely used in organic synthesis. This reagent is capable of converting primary and secondary alcohols into aldehydes and ketones, respectively. The Dess-Martin oxidation reaction is a highly selective oxidation reaction, and it can be used to oxidize a wide range of alcohols with high efficiency and low toxicity..
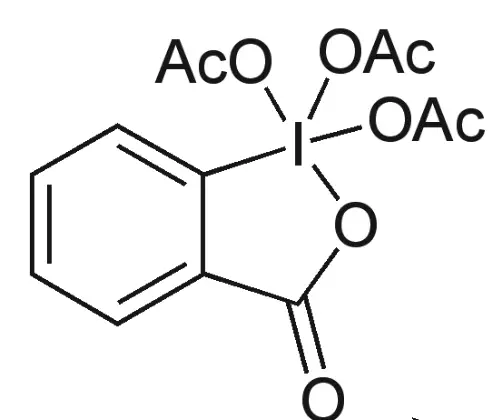
The Dess-Martin reagent is a combination of periodinane and a base, typically sodium hydroxide. The reagent is relatively expensive and relatively difficult to prepare, but it can be stored at room temperature and used for a long period of time. It is a colorless, liquid reagent that is stable under the reaction conditions, and it does not produce any toxic by-products..
The reagent is typically used as a solution in water or an organic solvent such as ethanol or methanol..
The periodinane molecule is an organoiodine compound formed by an iodine and a nitrogen atoms, which are connected by a carbon-carbon double bond. The chemical formula of periodinane is C5H6INO.
The structure of the periodinane molecule can be divided into two main parts: the iodine atom and the nitrogen atom. The iodine atom is located at the center of the molecule, and it is connected to the nitrogen atom by a carbon-carbon double bond. The iodine atom is also connected to a methyl group, which is composed of a carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms..
The nitrogen atom is located on one end of the molecule, and it is connected to the iodine atom by a double bond. The nitrogen atom is also connected to a methylene group, which is composed of a carbon atom and two hydrogen atoms. The nitrogen atom is also connected to a second iodine atom, which is connected to a methyl group..
The reactivity of periodinane is due to the presence of the iodine atom, which acts as an electrophile, and the nitrogen atom, which acts as a nucleophile. The electrophilic nature of the iodine atom allows it to react with the oxygen atom of the alcohol, and the nucleophilic nature of the nitrogen atom allows it to act as a base in the elimination step of the Dess-Martin oxidation reaction..