Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
What is urea?
Urea is a solid of molecular formula H2NCONH2 with a molar mass (60.024 g/mol). It has a density under normal conditions of 0.74 g/cm3. It has a melting point (mp = 132.7 ºC). It is very soluble in water (108 g of urea dissolve in 100 ml of H2O at a temperature of 20 ºC), it is also very soluble in alcohol but insoluble in chloroform and ether. The functional group of urea is also called carbamide or carbonyldiamide.
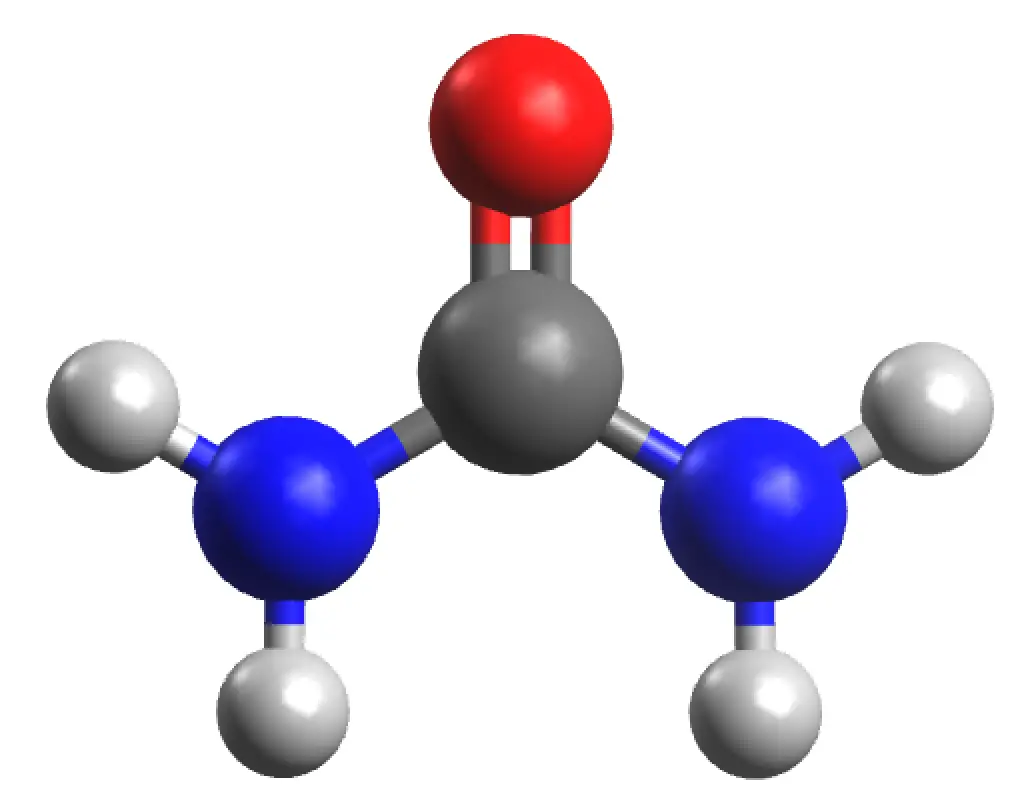 |
| 3D Structure |
When urea is heated to a temperature above its melting point it decomposes forming biuret, ammonia and cyanuric acid.
H2NCONH2 ⇌NH3 + HNCO →H2NCONH2H2NCONHCONH2 (biuret)
In 1828, the chemist Friedrich Wöhler synthesized this organic compound for the first time from another inorganic compound (ammonium cyanate), refuting the vitalist theory of Jacob Berzelius.
H4N⊕⊝O–C≡N →∆ H2NCONH2
Its main use is as a fertilizer and in animal feed.