What is Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction?
The Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction involves the α-halogenation of carboxylic acids in the presence of catalytic phosphorus. The reaction likely proceeds through the enol form of the intermediate acyl halide.
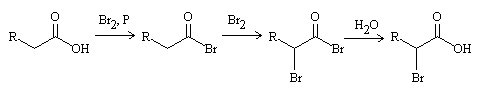
The discovery of this reaction is attributed to Carl M. von Hell (1849-1926), who first reported it in 1881. Jacob Volhard (1849-1909) and Nikolai D. Zelinsky (1861-1953) later made modifications and improvements to the reaction.
References
- Hell, C. (1881), Ueber eine neue Bromirungsmethode organischer Säuren. [On a new bromination method of organic acids.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 14: 891-893. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.188101401187
- Volhard, J. (1887), 4) Ueber Darstellung α-bromirter Säuren. [4) On the preparation of α-brominated acids.] Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem., 242: 141-163. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.18872420107
- Zelinsky, N. (1887), Ueber eine bequeme Darstellungsweise von α-Brompropionsäureester. [On a convenient mode of presentation of α-bromopropionic acid ester.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 20: 2026-2026. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.188702001452
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.