What is Craig 2-bromo-pyridine synthesis?
In 1915, Chichibabin and Ryasanjev reported the preparation of 2-bromopyridine from 2-aminopyridine, but the yield was low. Later, in 1934, Craig reported a modified method for producing high yields of 2-bromo-pyridine (α-position) from 2-amino-pyridine. As a result, this reaction is commonly referred to as the Craig 2-bromo-pyridine synthesis or Craig method.
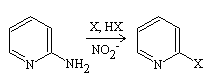
The Craig 2-bromo-pyridine synthesis involves adding a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium nitrite NaNO2 and 2-amino-pyridine to concentrated hydrobromic acid that has been saturated with bromine, followed by warming. To obtain an optimal yield of 2-bromo-pyridine, it has been suggested that at least 2 moles of bromine and 2.5 moles of sodium nitrite are required.
This method has been successfully employed for the preparation of both 2-bromo-pyridine and 2-bromo-pyrimidine.
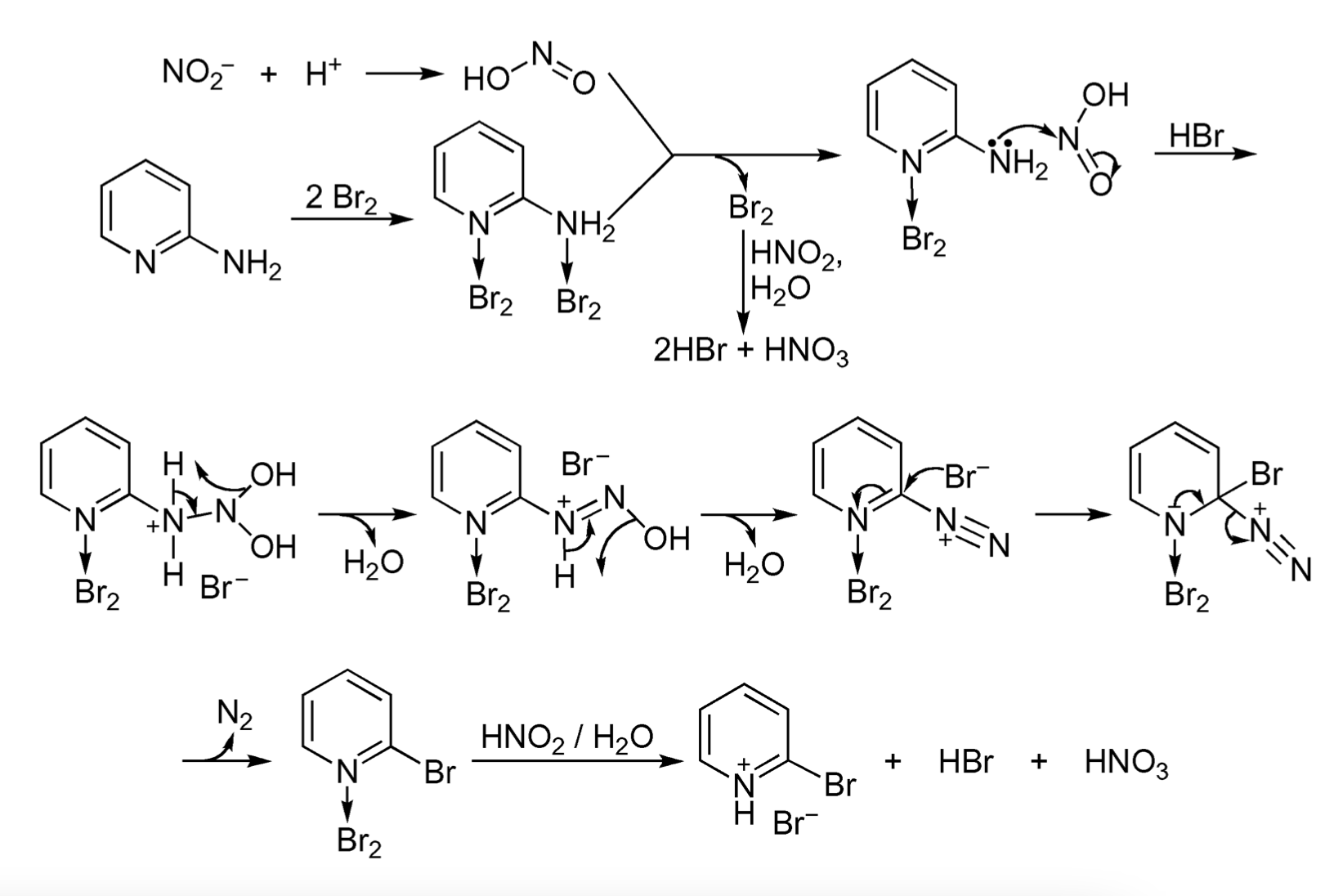
Mechanism of reaction
References
- Chichibabin, A. E. and Ryasanjev, M. D., J. Russ. Phys. Chem. Soc., 1915, 47, 1571.
- Lyman C. Craig “A Study of the Preparation of Alpha-Pyridyl Halides from Alpha-Aminopyridine by the Diazo Reaction”Journal of the American Chemical Society 1934 56 (1), 231-232
DOI: 10.1021/ja01316a072
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.