Objective
To perform a reductive amination in the solid phase.
Background
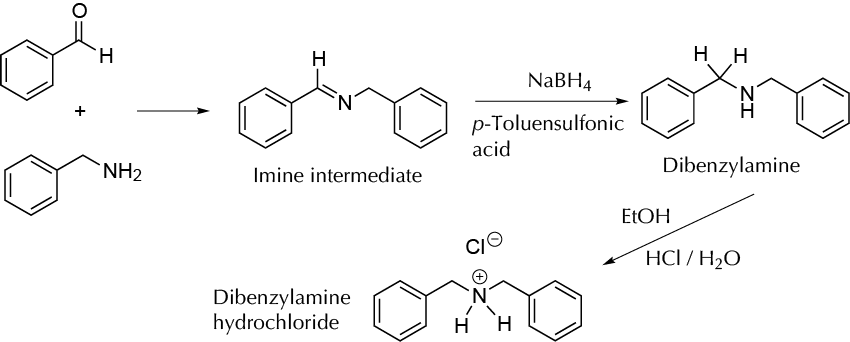
Reductive amination is the conversion of an aldehyde or a ketone into an amine via an intermediate imine. This reaction is considered the most remarkable way to synthesize complex amines, and a majority of amines prepared in the pharmaceutical industry are made by this procedure. This experiment consists of the synthesis of N-benzylamine by the reaction of equimolar amounts of benzaldehyde and benzylamine to give the corresponding imine, which is converted into the amine, roughly mixing the reagents in a mortar in a solvent-free transformation. The first step is to mix the reagents, and the second one is to add p-toluensulfonic acid and NaBH4. The transformation of reagents is easily detected by physical changes, which take place without solvent. The amine is isolated as N-benzylamine hydrochloride.
Experimental procedure
In a mortar and pestle, place 0.51 ml (approximately 5 mmol) of the benzaldehyde and bezylamine (0.58 ml, 5 mmol). Use a separate 1 ml syringe for each. Take turns gently mixing the reaction for 15 min until a solid (slushy consistency) forms. This indicates that the imine has formed. Weigh 5 mmol of p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA) and 5 mmol of NaBH4, and mix them together well in a watch glass with a glass rod. Put this solid mixture into the mortar, and take turns gently grinding for 25-30 min. Transfer the resulting mixture into a 50 or 100 ml beaker with a spatula, and wash the remaining material from the mortar and pestle into the beaker with 20 ml of 5 % NaHCO3. Transfer the solution to a separatory funnel and add 20 ml of ethyl acetate. Remove the aqueous layer and label the beaker with the aqueous layer for proper disposal later. Transfer the organic layer to a 50 ml Erlenmeyer, and dry the solvent by placing one or two scoops of potassium carbonate into the organic layer and swirling the container. Gravity filter by placing a filter paper and funnel into a previously weighed 50 ml round-bottom flask. Concentrate the product to dryness by placing the round-bottom flask on the rotary evaporator and removing the ethyl acetate. Measure the mass of the round-bottom flask containing the product. Add 5 ml of EtOH to the round-bottom flask, and transfer the product to a 25 ml Erlenmeyer flask using an automatic pipette. Dropwise add 0.5 ml of concentrated HCl. At this point, some crystals will form in the flask. When this occurs, collect the crystals by vacuum filtration using a Bühner or a Hirsch funnel, and keep the vacuum on for a few minutes until the crystalline salt is dry. Transfer the solid to a 25 ml Erlenmeyer flask, and recrystallize from EtOH (approximately 10 ml). Collect the purified crystals by vacuum filtration using a Hirsch funnel, washing them with 1-2 ml of EtOH, and allow them to air dry at least overnight. The next day, weigh the final salt and measure the m.p.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | -26 | 178-179 | 1.044 |
| Benzylamine | 107.15 | 10 | 184-185 | 0.981 |
| EtOH | 46.07 | -114.1 | 78.5 | 0.790 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| NaBH4 | 37.8 | 400 | - | 1.07 |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid | 172.2 | 106-107 | - | 1.240 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Benzaldehyde |  |
| Benzylamine |   |
| EtOH |  |
| HCl |   |
| NaBH4 |    |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Benzaldehyde | HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Benzylamine | WGQKYBSKWIADBV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| EtOH | LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaBH4 | YOQDYZUWIQVZSF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid | JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- S. W. Goldstein and A. V. Cross, Solvent-Free Reductive Amination: An Organic Chemistry Experiment, Journal of Chemical Education 07 (2015), no. 92, 1214—1216, DOI: 10.1021/ed5006618
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.