Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
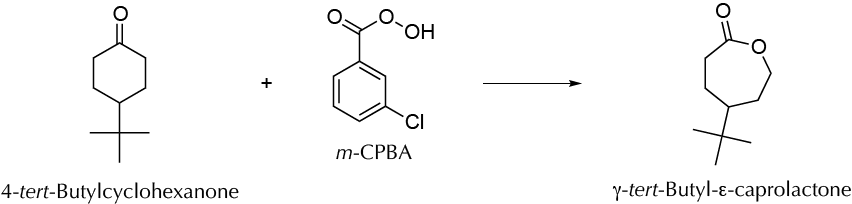
To synthesize a bulk chemical (γ-tert-butyl-ε-caprolactone) from a renewable feedstock (4-tert-butylcyclohexanone) by oxidation reaction.
Background
The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation is a rearrangement transformation of ketones to give esters. This is a suitable and efficient method to synthesize lactones from cyclic ketones in a one-step reaction. In this experiment, 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone is transformed into γ-tert-butyl-ε-caprolactone using m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (m-CPBA) as the oxidizing reagent under solvent-free conditions.
Experimental procedure
To a 50 ml round-bottom flask, add 0.5 g (3.2 mmol) of 4-tert-butylcyclohexanone and 1.12 g (6.5 mmol) of m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid. Immediately attach a reflux condenser to the flask. After approximately 2 min of heating, the crude reaction will begin to become warm and will bubble. Once the reaction has begun, stir the mixture every 5 min for 30 min. After this period, treat the reaction mixture with an aqueous solution of sodium bisulfite (20 ml of 20 % NaHSO3). Transfer the mixture to a separatory funnel and rinse the reaction flask with ether (2 × 20 ml). Transfer the ether extracts again to the separatory funnel and wash with portions of an aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (1.1 g of NaHCO3 in 200 ml of H2O) in a separatory funnel (4 × 50 ml). Dry the ether layer on anhydrous sodium sulfate Na2SO4. The desiccant is eliminated by gravity filtration on a tared round-bottom flask. Remove the ether by vacuum distillation (rotary evaporator) to give a solid residue. Wash the off-white residue with a small amount of cold pentane and collect the solid by vacuum filtration (m.p. = 57.5-58.5 ºC). Expected yields are in the 50-80 % range.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Diethyl ether | 74.12 | -116 | 34.6 | 0.71 |
| Hexane | 86.18 | -95 | 69 | 0.659 |
| MgSO4 | 120.37 | 1124 | - | 1.070 |
| NaHSO3 | 104.06 | - | - | 1.48 |
| NaHCO3 | 84.01 | 300 | - | 2.160 |
| Pentane | 72.15 | -130 | 36.1 | 0.626 |
| m-Chloroperbenzoic acid | 172.57 | 69-71 | - | - |
| 4-tert-Butylcyclohexanone | 154.25 | 113-117 | 225.1 | - |
| 4-tert-Butyl-ε-caprolactone | 170.25 | 57.5-58.5 | - | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Diethyl ether |   |
| Hexane |     |
| MgSO4 | Non-hazardous |
| NaHSO3 |   |
| NaHCO3 | Non-hazardous |
| Pentane |     |
| m-Chloroperbenzoic acid |   |
| 4-tert-Butylcyclohexanone |  |
| 4-tert-Butyl-ε-caprolactone |  |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Diethyl ether | RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hexane | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MgSO4 | CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| NaHSO3 | DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| NaHCO3 | UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Pentane | OFBQJSOFQDEBGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| m-Chloroperbenzoic acid | NHQDETIJWKXCTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 4-tert-Butylcyclohexanone | YKFKEYKJGVSEIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 4-tert-Butyl-ε-caprolactone | XFKCBMHHCWKGMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- J. J. Esteb, J. N. Hohman, D. E. Schlamadinger, and A. M. Wilson, A Solvent-Free Baeyer–Villiger Lactonization for the Undergraduate Organic Laboratory: Synthesis of γ-t-Butyl-ε-caprolactone, Journal of Chemical Education 82 (2005), no. 12, 1837 DOI: 10.1021/ed082p1837