Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
To obtain benzoic acid by oxidation of alkyl functional groups from aromatic compounds using potasium permanganate (KMnO4).
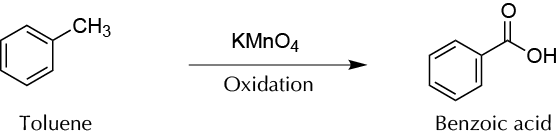
Background
The alkyl chains attached to aromatic rings are likely to be oxidized to acid if they have at least one hydrogen at the benzyl position. Permanganate is an oxidizing agent widely used both in organic and inorganic reactions. Permanganate, which has a very distinctive purple color is reduced to MnO2, which is brown and insoluble in water. If the reaction is carried out in a basic medium the acid is present as a salt, so it is soluble in an aqueous medium. If the aromatic ring presents more than one alkyl chain with at least one hydrogen at the benzyl position, it will be produced as many carboxylic groups as chains has the molecule.
Microscale experimental procedure
In a conical vial of 5 ml provided with a spin vane, add in this order 825 mg of potassium permanganate KMnO4, 100 mg of sodium carbonate, and 3 ml of water. Couple a condenser and gently heat the mixture until all reagents are dissolved. Then disconnect the plate, allow to cool sightly and add 250 μl of toluene and 10 mg of liquid detergent. Reflux the mixture with stirring for 45 min. Afterward, the purple color of the permanganate will turn to brown from MnO2. Upon reflux completion, allow the reaction to cool without reaching r.t., disconnect the condenser while still hot, and add dropwise a solution of NaHSO3 until complete disappearance of the purple color. Filter the reaction crude under vacuum with a Hirsch funnel on a 10 ml Erlenmeyer. Wash the solid with 1 ml additional water. Cool the filtrate with an ice-water bath and add HCl (conc.) dropwise until the pH reaches approximately 2.0 (test with indicator paper). A white precipitate corresponding to benzoic acid appears. Filter the crystals with a Hirsch funnel, dry weigh, and calculate the yield.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Benzoic acid | 122.12 | 125 | 249 | 1.08 |
| Celite® S | - | - | - | - |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| KMnO4 | 158.04 | 240 | - | 2.71 |
| MnO2 | 86.49 | 535 | - | 5.026 |
| Na2CO3·10H2O | 286.14 | 32-34 | - | 1.44 |
| NaHSO3 | 104.06 | - | - | 1.48 |
| Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate | 348.48 | - | - | - |
| Toluene | 92.14 | -93 | 110.6 | 0.867 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Benzoic acid |   |
| Celite® S |  |
| HCl |   |
| KMnO4 |    |
| MnO2 |  |
| Na2CO3·10H2O |  |
| NaHSO3 |   |
| Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate |   |
| Toluene |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Benzoic acid | WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Celite® S | |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| KMnO4 | VZJVWSHVAAUDKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MnO2 | NUJOXMJBOLGQSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Na2CO3·10H2O | XYQRXRFVKUPBQN-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| NaHSO3 | DWAQJAXMDSEUJJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate | VQOIVBPFDDLTSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Toluene | YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- C. F. Cullis and J. W. Ladbury, Kinetic studies of the oxidation of aromatic compounds by potassium permanganate. Part IV. n- and iso-Propylbenzene, Journal of the Chemical Society (1955), 4186–4190, DOI 10.1039/JR9550004186