Objective
To perform at microscale the addition of HBr to an alkene (hex-1-ene) to yield 2-bromohexane under phase-transfer catalyst conditions.
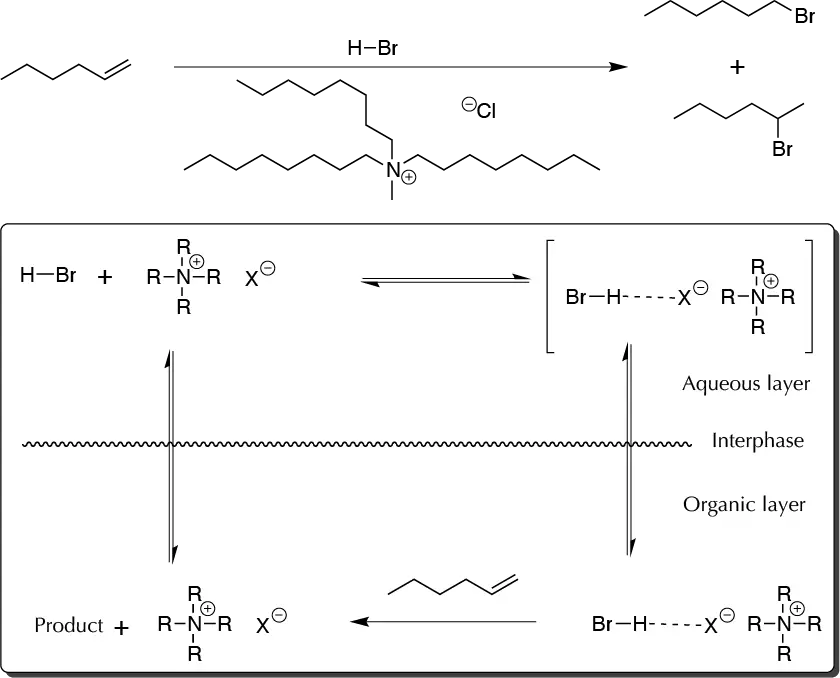
Background
Electrophilic addition ot HX to alkenes is a useful reaction for functional group interconversions. The reaction begins by a proton attack on the double bound and formation of a carbocation. These reactions are controlled by the Markovnicov rule, which indicates that the product is formed from the most stable carbocation. When this reaction is performed, certain practical problems arise. Most of alkenes are insoluble in such a polar medium as concentrated HBr, and water present in the reaction media causes the hydration reaction of the alkene to compete with the main reaction. This problem is avoided by using a phase-transfer catalyst, which improves the contact between the HBr and the alkene.
Microscale experimental procedure
Place 500 μl of hex-1-ene in a 5 ml conical vial with a spin vane, with 2 ml of 48% aqueous HBr and 150 mg of tricaprylmethylammonium chloride (Aliquat 33®). Set a water-jacketed condenser and reflux the reaction with magnetic stirring for 2 h. Cool the reaction mixture to room temperature and add 1 ml of hexane. Remove the condenser and set a stopper. Shake the vial by hand for 1 min, and then let the two layers separate. Remove the aqueous layer (lower) with a Pasteur pipette.
Wash the remaining organic layer with 2 ml of 10% solution of NaHCO3, shaking the uncovered vial to avoid CO2 accumulation. The operation is repeated until ensuring that no more acid remains in the organic layer (the pH paper test of the aqueous layer must be basic). With a microspatula, add anhydrous Na2SO4 until the solution becomes transparent, indicating that all water has been removed.
Finally, transfer the organic solution to a clean 5 ml conical vial with a Pasteur pipette, fit a Hickman column, and proceed to distill (b.p. = 166–167 ºC). Carefully transfer the distillate to a tared clean and dry vial to calculate the yield.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Hexane | 86.18 | -95 | 69 | 0.659 |
| NaHCO3 | 84.01 | 300 | - | 2.160 |
| Hex-1-ene | 84.16 | -140.0 | 60-66 | - |
| HBr | 80.91 | -87 | -67 | 2.140 |
| Aliquat® 336 | - | -6 | - | - |
| Na2SO4 | 142.04 | 884 | - | 2.630 |
| CO2 | 44.01 | -78.5 | - | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Hexane |     |
| NaHCO3 | Non-hazardous |
| Hex-1-ene |   |
| HBr |    |
| Aliquat® 336 |    |
| Na2SO4 | Non-hazardous |
| CO2 |  |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Hexane | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaHCO3 | UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Hex-1-ene | LIKMAJRDDDTEIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HBr | CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Aliquat® 336 | |
| Na2SO4 | PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| CO2 | CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- R. A. W. Johnstone, A. H. Wilby, and I. D. Entwistle, Heterogeneous catalytic transfer hydrogenation and its relation to other methods for reduction of organic compounds, Chemical Reviews 85 (1985), no. 2, 129–70, DOI: 10.1021/cr00066a003