Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
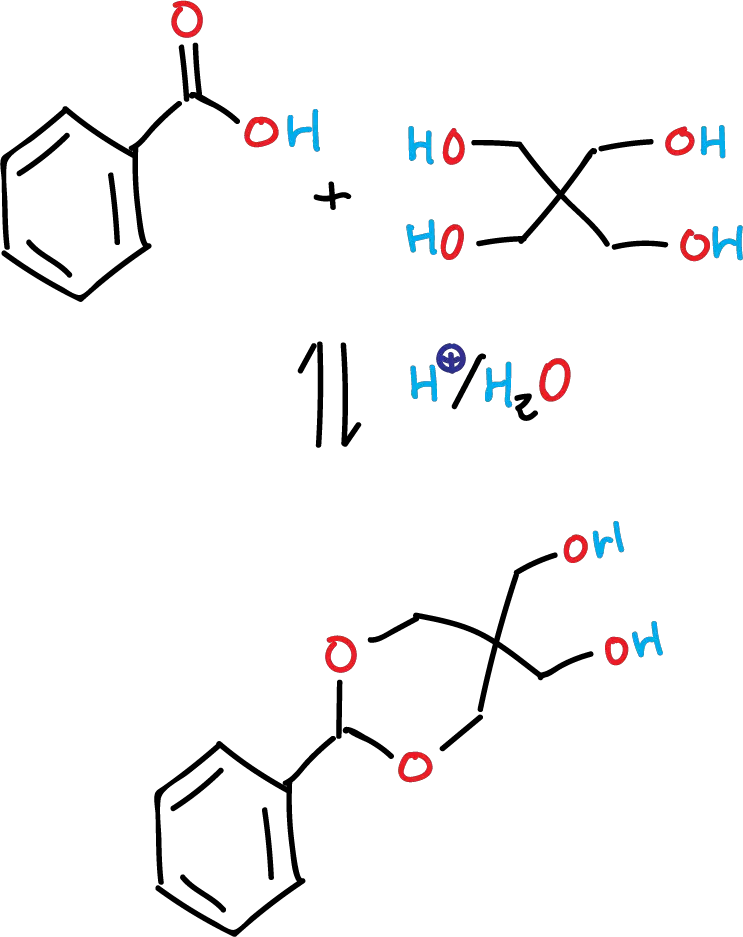
To synthesize an acetal (5,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-phenyl-1,3-dioxane) from benzaldehyde in aqueous media.
Background
Acetals are common carbonyl compound derivatives that are often used in Organic Synthesis as protecting groups for aldehydes and ketones, as well as in many other reactions.
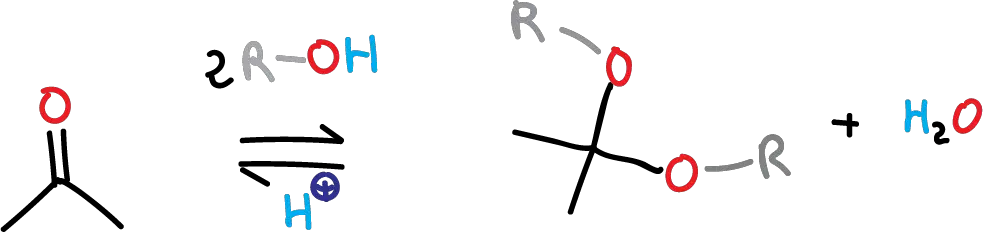
Cyclic acetals are formed by the acid-catalyzed reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a diol —e.g., ethylene glycol. The formation of acetals and ketals entails a dehydration process, because a water molecule is formed from the starting materials. The reaction is an equilibrium process that is usually performed in an organic solvent, in which water is removed from the reaction to shift the equilibrium toward product formation.
Despite this, in this experiment, acetal formation is performed in water with pentaerythritol and benzaldehyde in the presence of an acid. The reaction takes place with good yields, owing to the insolubility of the final product in the aqueous reaction medium. Two remaining hydroxyl groups remain unreacted in the pentaerythritol moiety.
Experimental procedure
Pentaerythritol (1.8 g, 13 mmol) and water (26 ml) are placed in a 50 ml round-bottom flask or Erlenmeyer flask equipped with a magnetic stir bar and a thermometer. The solid is dissolved by gently heating the mixture to 35 ºC in a water bath on a hot plate/stirrer. Upon dissolution of pentaerythritol, concentrated HCl (2 drops, 0.1 ml) is added, followed by benzaldehyde (1.4 ml, 14 mmol). The mixture is heated at 35 ºC for 1 h, during which a solid precipitates. The solid is filtered under vacuum and washed with 1 ml of cold water and air-dried in the filter. Recrystallization of the solid from 12 ml of toluene gives 5,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2-phenyl-1,3-dioxane, as a colorless solid, which is air-dried on the filter. The recrystallized final product gives an m.p. of 135-137 ºC (134–135 ºC).
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | -26 | 178-179 | 1.044 |
| Oxone® | 614.78 | - | - | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Benzaldehyde |  |
| Oxone® |     |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Benzaldehyde | HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Oxone® | HJKYXKSLRZKNSI-UHFFFAOYSA-I |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- D. M. Collard, A. G. Jones, and R. M. Kriegel, Synthesis and spectroscopic analysis of a cyclic acetal: a dehydration performed in aqueous solution, Journal of Chemical Education 78 (2001), no. 1, 70–72, DOI: 10.1021/ed078p70