Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
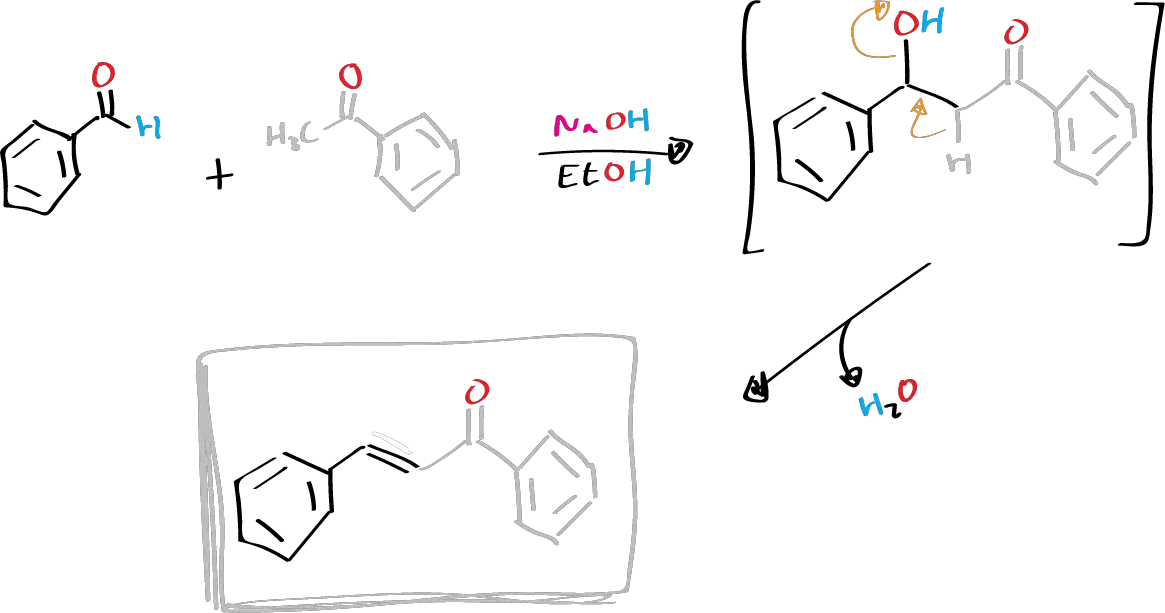
To obtain chalcone using the Claisen-Schmidt condensation by condensing an aromatic aldehyde with a ketone in the presence of a base.
Background
The Claisen-Schmidt condensation is a type of aldol condensation that involves synthesizing α,β-unsaturated ketones by condensing a ketone with an aromatic aldehyde.
This reaction is possible because the aromatic aldehyde lacks hydrogens in the α-position relative to the carbonyl group, which prevents self-condensation but enables it to react with the ketone. However, it is not possible to isolate the initial aldolization adduct because it dehydrates spontaneously under the reaction conditions.
Experimental procedure
To perform this chemical reaction, first dissolve 1 g of sodium hydroxide in 22 ml of ethanol. Next, in a 100 ml erlenmeyer flask, pour 1.25 ml of benzaldehyde and add 0.9 ml of acetophenone using a pipette. Then, add the alkaline ethanolic solution to the flask, stopper the erlenmeyer and shake (stir bar) at 25°C for 24 hours. After stirring, remove the solvent using a rotary evaporator to obtain a solid.
Wash the solid with 2 x 30 ml of tert-butyl methyl ether (CH3)3COCH3. The resulting ether solution should be washed with 6 x 30 ml of water and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. Filter the mixture to remove the Na2SO4 and remove the solvent using a rotary evaporator. Recrystallize the residue obtained using hexane/(CH3)3COCH3.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Styrene | 104.15 | -31 | 145-146 | 0.906 |
| Chalcone | 208.26 | 55-57 | 345-348 | 1.071 |
| Acetophenone | 120.15 | 19-20 | 202 | 1.03 |
| Benzaldehyde | 106.12 | -26 | 178-179 | 1.044 |
| NaOH | 40.00 | 318 | 1,390 | 2.130 |
| EtOH | 46.07 | -114.1 | 78.5 | 0.790 |
| Hexane | 86.18 | -95 | 69 | 0.659 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Styrene |   |
| Chalcone |  |
| Acetophenone |  |
| Benzaldehyde |  |
| NaOH |  |
| EtOH |  |
| Hexane |     |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Styrene | PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Chalcone | DQFBYFPFKXHELB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetophenone | KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Benzaldehyde | HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaOH | HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| EtOH | LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hexane | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145
- D. R. Palleros, Solvent-free synthesis of chalcones, Journal of Chemical Education 81 (2004), no. 9, 1345, DOI: 10.1021/ed081p1345