Objective
to obtain and characterize an oxime (acetophenone oxime) by reacting acetophenone with hydroxylamine hydrochloride in the presence of sodium acetate and ethanol.
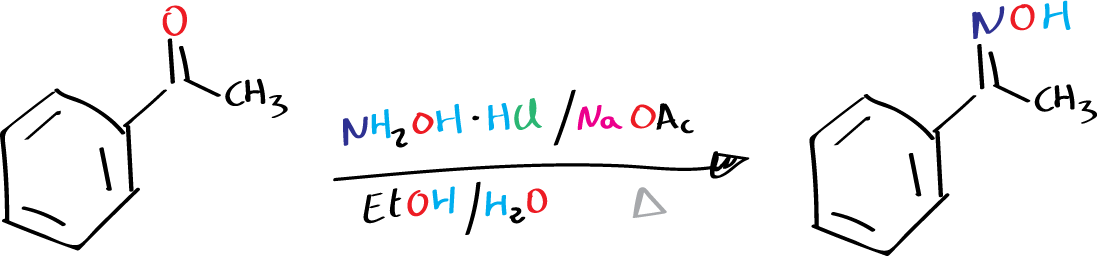
Background
Oximes are organic compounds that contain the functional group -C=N-OH. They are synthesized by the reaction of a carbonyl compound (>C=O) with hydroxylamine NH2OH or its derivatives. The resulting product is an addition product, which undergoes dehydration to form the oxime.
Acetophenone oxime is one of the commonly synthesized oximes in chemical laboratories. It is synthesized by reacting acetophenone with hydroxylamine hydrochloride in the presence of a base (NaOAc) and ethanol.
Experimental procedure
To prepare the oxime, first, dissolve the acetophenone (1.2 g, 10 mmol) in 20 mL of EtOH in a 50 mL round‐bottom flask. Then, add the hydroxylamine hydrochloride NH2OH·HCl (1.18 g, 17 mmol) and sodium acetate trihydrate (0.82 g, 10 mmol), which should already be dissolved in 15 mL of warm water, to the flask.
Heat the mixture under reflux on a water bath for 20 minutes. After that, quickly filter the hot solution through a fluted filter paper. To collect the crystalline oxime (a white crystalline solid), cool the filtrate in an ice bath and filter it under vacuum. Wash the crystals with a small volume of cold 50 % EtOH and dry them on the filter with suction. Finally, record the yield and melting point of the product.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetophenone | 120.15 | 19-20 | 202 | 1.03 |
| Hydroxylamine hydrochloride | 69.49 | 155-157 | - | 1.670 |
| Sodium acetate trihydrate | 136.08 | - | - | - |
| EtOH | 46.07 | -114.1 | 78.5 | 0.790 |
| Acetophenone oxime | 135.16 | 55-60 | 118-120 | 1.110 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetophenone |  |
| Hydroxylamine hydrochloride |     |
| Sodium acetate trihydrate | Non-hazardous |
| EtOH |  |
| Acetophenone oxime |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetophenone | KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hydroxylamine hydrochloride | WTDHULULXKLSOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Sodium acetate trihydrate | AYRVGWHSXIMRAB-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| EtOH | LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetophenone oxime | JHNRZXQVBKRYKN-VQHVLOKHSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145