What is Claisen condensation?
The Claisen condensation, which is also referred to as the acetoacetic ester condensation, was discovered by Geuther in 1863 and later studied by Rainer Ludwig Claisen (1851-1930) in 1887. This chemical process involves the self-condensation of an ester in the presence of an alkali alkoxide in an alcohol solvent, resulting in the formation of β-keto esters, such as ethyl acetoacetate from ethyl acetate.
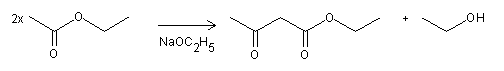
Typically, the Claisen condensation is conducted under basic conditions, utilizing reagents such as sodium ethoxide NaOEt, to produce β-keto esters from aliphatic carboxylic acid esters. This reaction is useful for synthesizing various types of β-keto esters, including both branched and unbranched varieties. In addition, ethyl acetoacetate, a commonly used β-keto ester, can be employed in the preparation of γ-diketones by reacting it with epoxides, followed by oxidation and decarboxylation.
The Claisen condensation involves the reaction of a compound called an “enolate” with a compound containing a carbonyl group, such as a ketone or an aldehyde. The reaction is typically carried out in the presence of a base, such as sodium ethoxide NaOEt, and a solvent, such as ethanol..
One of the advantages of the Claisen condensation is its high yield and efficiency. It is a relatively simple reaction that can be carried out under mild conditions and does not require the use of expensive or specialized reagents..
The Claisen condensation has a wide range of applications in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other chemicals. It has also been used in the synthesis of natural products, such as flavonoids and terpenoids..
Summary
The Claisen condensation is a valuable tool for the synthesis of esters and has played an important role in the development of a number of important chemical compounds..
Example
The Claisen condensation is a chemical reaction between two esters or an ester and an aldehyde to form a β-keto ester or a β-diketone, respectively, with the release of a small molecule such as water or methanol..
One example of a Claisen condensation is the reaction between ethyl acetate and propionaldehyde to form 3-phenylpropionate. The reaction occurs in the presence of a base, such as sodium ethoxide, and proceeds through the formation of an intermediate ester enolate, which then undergoes a nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic aldehyde to form the β-keto ester product..
Overall, the reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Ethyl acetate + Propionaldehyde -> 3-Phenylpropionate + Water
This reaction is an important synthetic tool in organic chemistry and is widely used in the preparation of a variety of compounds, including flavors, fragrances, and pharmaceuticals..
Mechanism of reaction
The mechanism of the Claisen condensation can be divided into three main steps:
- Formation of the ester enolate: The first step in the Claisen condensation is the formation of an enolate ion from the ester starting material. This is typically achieved by reacting the ester with a strong base, such as sodium ethoxide NaOEt, to produce a nucleophilic enolate ion..
- Nucleophilic attack: The enolate ion then undergoes a nucleophilic attack on the electrophilic aldehyde, which results in the formation of an intermediate compound known as an acylium ion..
- Deprotonation: The acylium ion is then deprotonated by the base to form the β-keto ester product. This step is accompanied by the release of a small molecule, such as water or methanol, which is produced by the abstraction of a proton from the base..
Overall, the reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Ethyl acetate + Propionaldehyde -> 3-Phenylpropionate + Water
References
- Geuther, A. (1863), Untersuchungen über die einbasischen Säuren. [Studies on the monobasic acids.] Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem., 166: 97-110. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.18631660202
- Claisen, L. and Lowman, O. (1887), Ueber eine neue Bildungsweise des Benzoylessigäthers. [On a new way of forming benzoyl acetate.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 20: 651-654. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.188702001149