What is Duff reaction?
The Duff reaction, also known as the Duff formylation or Duff synthesis, was reported by Duff and Bills in 1932. It involves the formylation of phenols or aromatic amines in a mixture of hexamethylenetetramine (HMT), boric acid H3BO3, and glycerol (see list of acronyms).
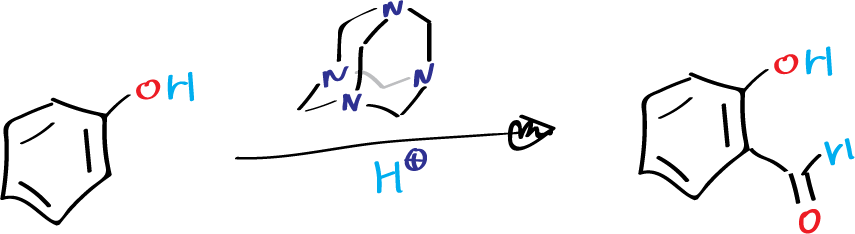
The Duff reaction typically proceeds very quickly and produces only ortho-formylated products (or occasionally small amounts of ortho, para-disubstituted products) in the case of phenols.
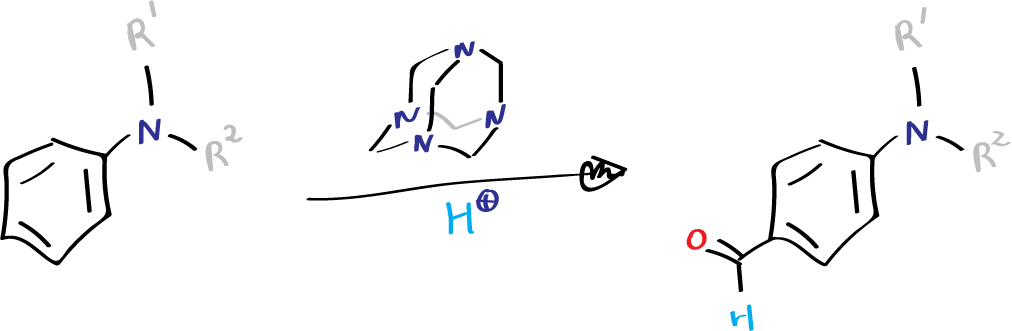
However, anilines yield para-products using this procedure. It has been observed that electron-withdrawing groups can hinder or prevent the reaction from occurring, which means that hydroxypyridines and hydroxyquinolines are not suitable for formylation using this method.
Mechanism of reaction
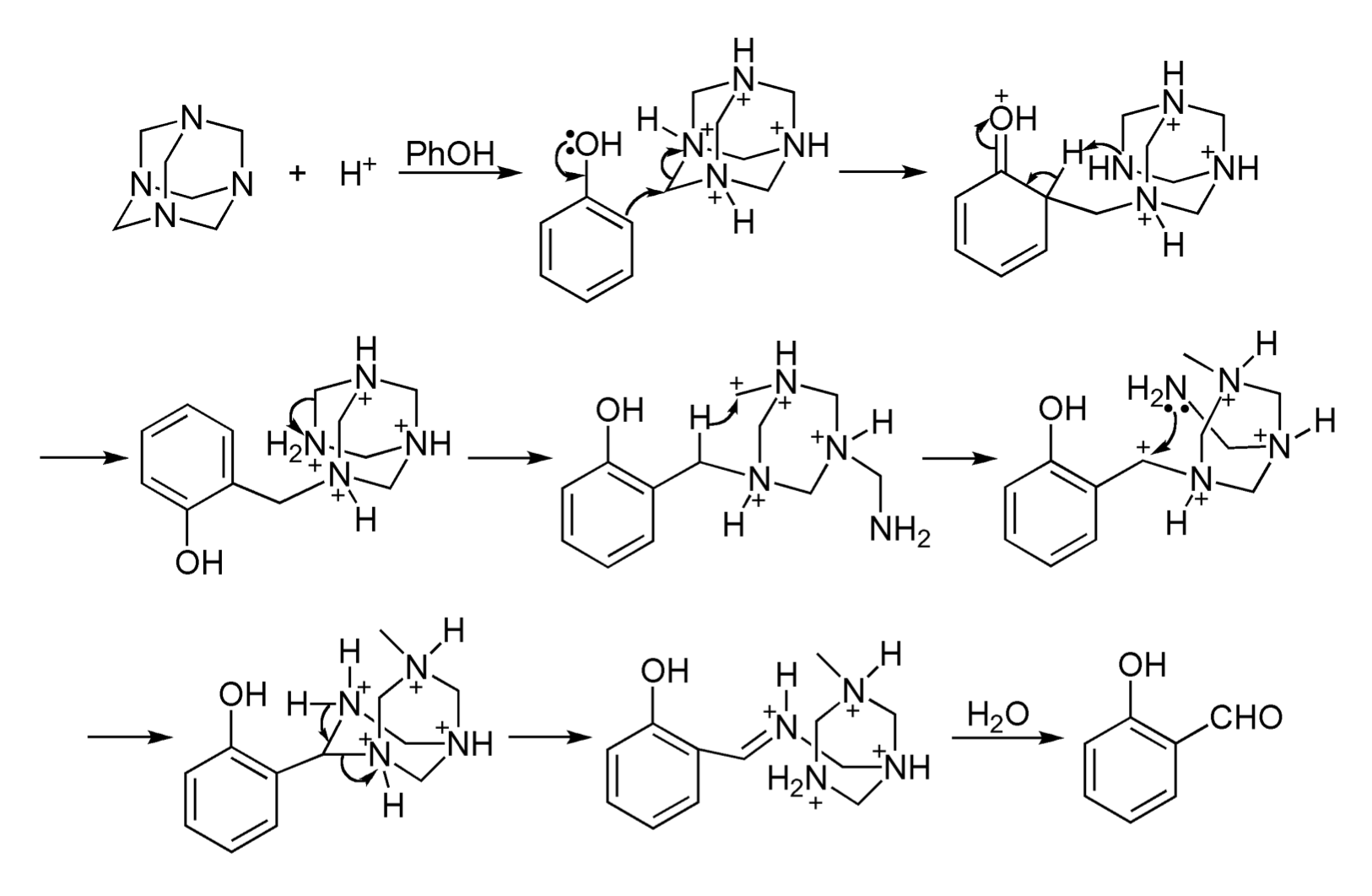
References
Duff, J. C.; Bills, E. J. “Reactions between hexamethylenetetramine and phenolic compounds. Part I. A new method for the preparation of 3- and 5-aldehydosalicylic acids” J. Chem. Soc., 1932, 1987-1988
DOI: 10.1039/JR9320001987
Full Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Granada, with a long-standing research career in Computational Chemistry and molecular modeling and design.