Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
To provide an example of multi-step synthesis (using protecting groups) by preparing an organic compound, benzocaine, that is present in many consumer products.
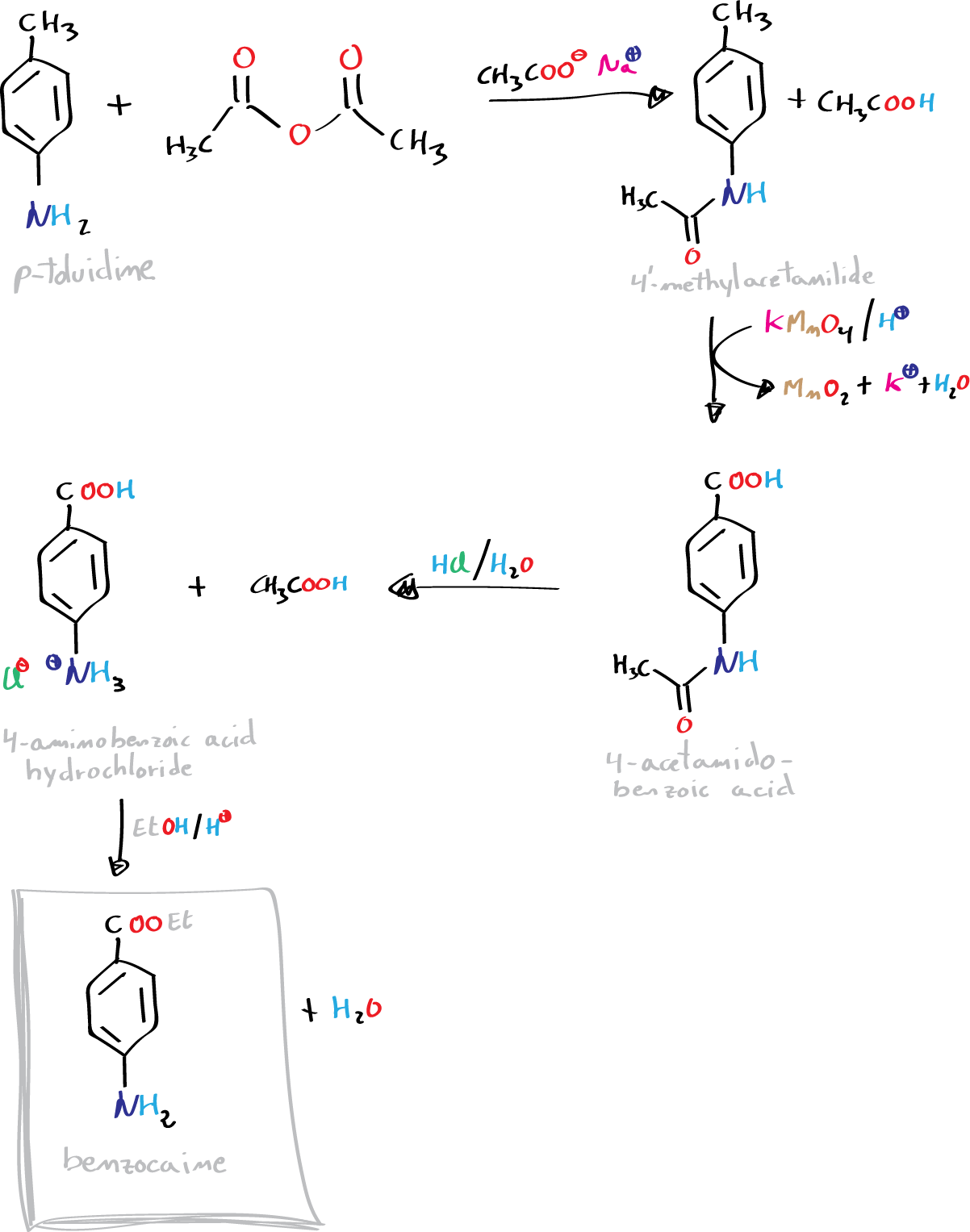
Background
Benzocaine (ethyl 4-aminobenzoate) is an anesthetic that is also used to relieve the pain of injuries and burns. Benzocaine is the derivative of p-aminobenzoic acid and can be synthesized via the Fischer esterification reaction. It can be prepared from p-toluidine by a four-step synthesis. The problem of a synthesis of this type is that the overall yield of the final product is usually quite low.
Experimental procedure
A) Synthesis of 4′-methylacetanilide:
Place 4 g of p-toluidine in a 100 ml Erlenmeyer flask. Then, in a fume hood, add 10 ml of acetic anhydride and slowly stir. The reaction is highly exothermic. Allow the reaction mixture to stand for 10 min and then pour the reaction crude onto 50 ml of water/ice. If the reaction mixture crystallizes in the flask, drag the solid with a small amount of cold water. Stir the suspension of the product in water with a rod, and then collect the resulting solid by vacuum filtration. Keep the product (4′-methylacetanilide or N-acetyl-p-toluidine) to carry out the next stage of the synthesis.
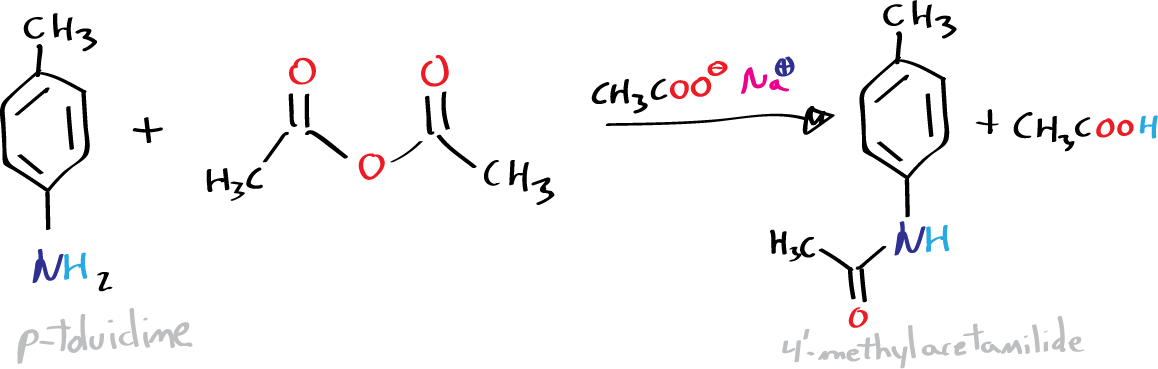
B) Synthesis of p-acetamidobenzoic acid:
In a 400 ml beaker place 4′-methylacetanilide (N-acetyl-p-toluidine), 200 ml of water, and an amount of 1.8 g KMnO4 per gram of N -acetyl-p-toluidine. In a water bath with magnetic stirring, heat the mixture until it acquires a distinct brown (approximately 30 min). Vacuum filter the resulting hot solution. If the filtered solution has a violet color, add EtOH dropwise, and heat gently until the color disappears. When the filtrate is colorless or slightly yellow, allow to cool and acidify with H2SO4 (20%). Vacuum filter the resulting white solid.
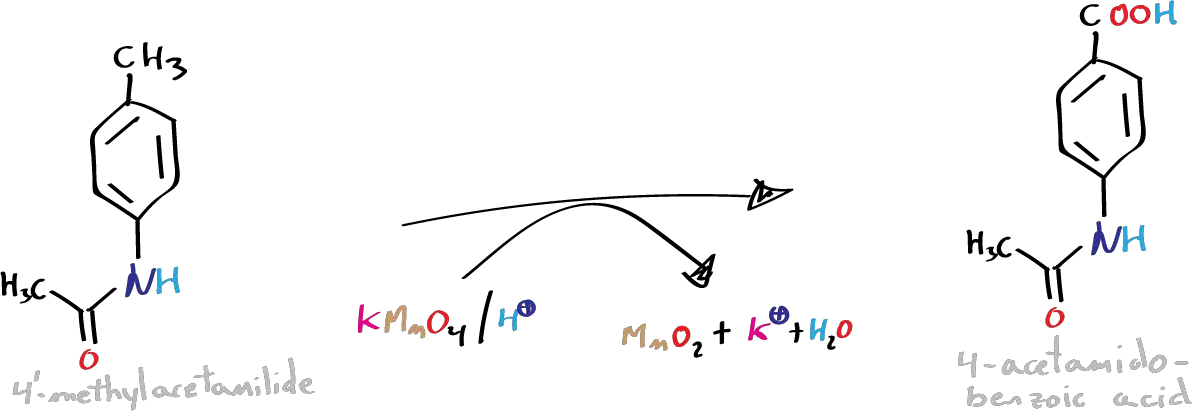
C) Synthesis of p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride:
Assemble the reflux in a flask of 100 ml and provide with a gas outlet to a trap with a diluted NaOH solution. Heat the flask for 30 min with a mixture of 2.5 g of p-acetamidobenzoic acid and 25 ml of HCl (conc.). Cool and collect the precipitate of p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride by vacuum filtration.
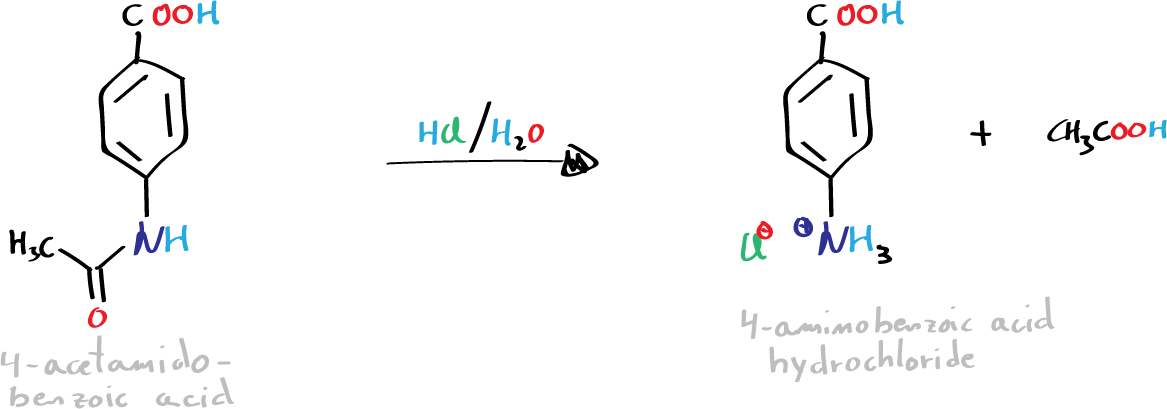
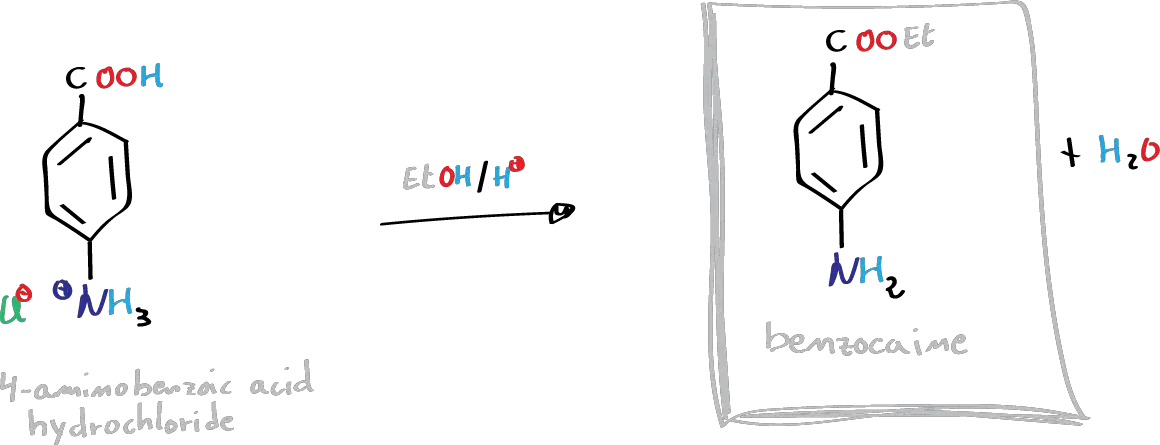
D) Synthesis of benzocaine:
Into a 100 ml flask, mix 1.25 g of p-aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride, 10 ml of EtOH, and 0.5 ml H2SO4 (conc.). Heat the mixture at reflux for 2 h. After cooling the mixture, neutralize with an aqueous sodium carbonate solution (10%). Extract with CH2Cl2 (3 × 5 ml), dry the organic layer with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporate in a rotary evaporator. Recrystallize the solid resulting from the EtOH/water.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| 4'-Methylacetanilide | 149.19 | 149-151 | 307 | - |
| Acetic anhydride | 102.09 | -73.1 | 139.8 | 1.080 |
| Benzocaine | 165.19 | 88-90 | - | - |
| CaCO3 | 100.09 | 800 | - | 2.93 |
| CH2Cl2 | 84.93 | -97 | 40.0 | 1.33 |
| EtOH | 46.07 | -114.1 | 78.5 | 0.790 |
| H2SO4 | 98.08 | 3 | - | 1.80-1.84 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| KMnO4 | 158.04 | 240 | - | 2.71 |
| Na2SO4 | 142.04 | 884 | - | 2.630 |
| NaOH | 40.00 | 318 | 1,390 | 2.130 |
| p-Acetamidobenzoic acid | 179.17 | 259-262 | - | - |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid | 137.14 | 187-189 | - | 1.374 |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride | 173.60 | - | - | - |
| p-Toluidine | 107.15 | 41-46 | 200 | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| 4'-Methylacetanilide |  |
| Acetic anhydride |    |
| Benzocaine | Non-hazardous |
| CaCO3 | Non-hazardous |
| CH2Cl2 |  |
| EtOH |  |
| H2SO4 |  |
| HCl |   |
| KMnO4 |    |
| Na2SO4 | Non-hazardous |
| NaOH |  |
| p-Acetamidobenzoic acid | Non-hazardous |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid |  |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride |  |
| p-Toluidine |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| 4'-Methylacetanilide | YICAMJWHIUMFDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetic anhydride | WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Benzocaine | BLFLLBZGZJTVJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CaCO3 | VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| CH2Cl2 | YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| EtOH | LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H2SO4 | QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| KMnO4 | VZJVWSHVAAUDKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Na2SO4 | PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| NaOH | HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| p-Acetamidobenzoic acid | QCXJEYYXVJIFCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid | ALYNCZNDIQEVRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Aminobenzoic acid hydrochloride | KBCPMQUSOLSAQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Toluidine | RZXMPPFPUUCRFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- P. Demare and I. Regla, Synthesis of two local anesthetics from toluene: an organic mul- tistep synthesis in a project-oriented laboratory course, Journal of Chemical Education 89 (2012), no. 1, 147–149, DOI: 10.1021/ed100838a