Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
To perform a reductive amination of a carbonyl compound, emulating the biosynthesis of an amino acid but without using enzyme catalysis.
Background
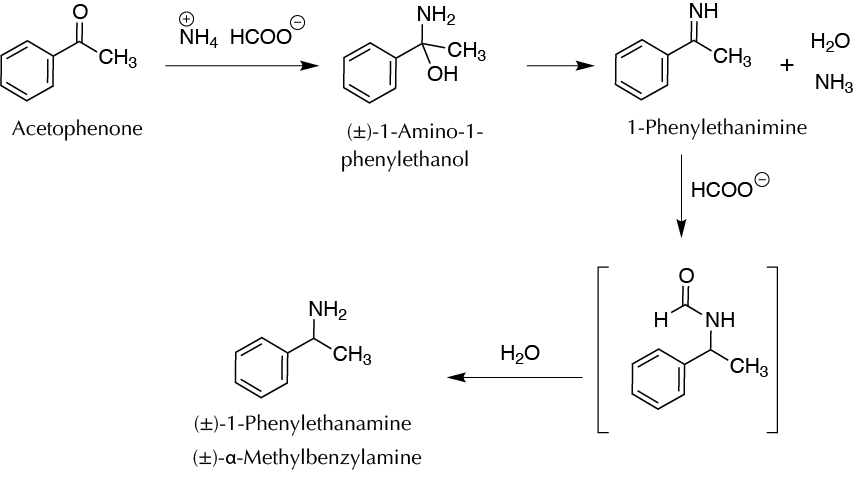
When reagents, products, and non-chiral catalysts are used in a chemical reaction, the overall result is an optically inactive mixture. However, if a center or chiral carbon has been generated, the product will invariably appear as a racemic mixture (50% of the two possible enantiomers). In nature, optically active compounds are generated by means of enzymatic catalysis, producing only one of the two enantiomers (enantiospecific reaction). In this experiment, a reductive amination is performed by reacting a carbonyl compound (acetophenone) with ammonia, which acts as the nucleophile being added to the carbonyl group and generates an aminoalcohol that dehydrates, giving an imine. This imine is subsequently reduced with formate ion to the corresponding amine (Leuckart-Wallach reaction).
Experimental procedure
In a 100 ml round-bottom flask, add 25 g of acetophenone, 43 g of ammonium formate (NH4HCO2), and a magnetic stir bar. Assemble simple distillation equipment. Heat the mixture with a silicone bath, ensuring that the bath temperature does not exceed 200 ºC. On the neck of the Erlenmeyer collector, place cotton impregnated with H2SO4 diluted to prevent the escape of ammonia vapors. Continue heating until no distillate is collected. Cool the flask and then add 25 ml of water. Transfer the reaction mixture to a separatory funnel and extract with toluene (2 × 25 ml). Mix the toluene extracts with the above distillate and discard the aqueous layer.
Place in a flask equipped for simple distillation. Add 20 ml of concentrated HCl. Heat the mixture until all the toluene is distilled, taking care to collect on a glass with enough water so that the distillation gases bubble. Then, continue to heat for 40 min more, and allow the mixture to reach r.t. If some crystals form, add the minimum amount of water to dissolve. Extract the mixture with toluene (3 × 20 ml) and transfer the aqueous layer to a round-bottom flask. Add 43 ml of a solution of NaOH 50% and conduct simple distillation. Continue to distill until the pH of the distillate has no basic pH value (approximately 150 ml). Extract the distillate containing the amine with toluene (3 × 15 ml). Dry the toluene extract with NaOH pellets. Once dry, submit the solution to a simple distillation and the product distilled between 180–190 ºC is collected
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetophenone | 120.15 | 19-20 | 202 | 1.03 |
| H2SO4 | 98.08 | 3 | - | 1.80-1.84 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| NaOH | 40.00 | 318 | 1,390 | 2.130 |
| NH3 | 17.03 | -78 | -33 | 0.590 |
| Ammonium formate | 63.06 | 119-121 | - | 1.260 |
| R-(+)-α-methylbenzylamine | ||||
| S-(-)-α-methylbenzylamine | ||||
| Toluene | 92.14 | -93 | 110.6 | 0.867 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetophenone |  |
| H2SO4 |  |
| HCl |   |
| NaOH |  |
| NH3 |     |
| Ammonium formate |  |
| R-(+)-α-methylbenzylamine |   |
| S-(-)-α-methylbenzylamine |   |
| Toluene |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetophenone | KWOLFJPFCHCOCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H2SO4 | QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaOH | HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| NH3 | QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Ammonium formate | VZTDIZULWFCMLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| R-(+)-α-methylbenzylamine | RQEUFEKYXDPUSK-SSDOTTSWSA-N |
| S-(-)-α-methylbenzylamine | RQEUFEKYXDPUSK-ZETCQYMHSA-N |
| Toluene | YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145
- A. W. Ingersoll, J. H. Brown, C. K. Kim, W. D. Beauchamp, and G. Jennings, Extensions of the Leuckart synthesis of amines, Journal of the American Chemical Society 58 (1936), no. 9, 1808–1811, DOI: 10.1021/ja01300a089