Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
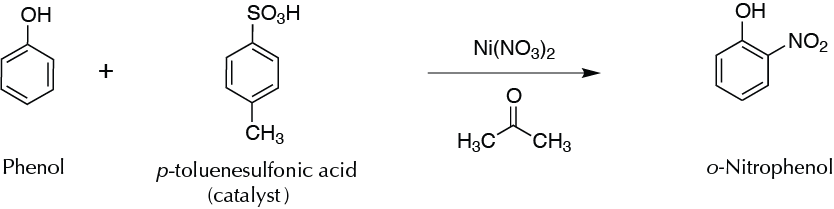
Regiospecific preparation of o-nitrophenol using Ni(NO3)2 and p-toluenesulfonic acid.
Background
Conventional reactions of nitration of aromatic compounds involve the use of HNO3 as the nitrating agent in the presence of H2SO4. In this experiment a nitration process that is fast and regiospecific and that has low environmen- tal impact is proposed. The reaction is performed with nickel nitrate and is catalyzed with p-toluenesulfonic acid in acetone. Under these conditions, the nitration of phenol occurs only at the orto-position with respect to the hydroxyl group. The reaction can be performed both at room temperature and at reflux, although to reflux, the reaction time is relatively short.
Experimental procedure
In a 100 ml round-bottom flask provided with a stir bar, dissolve 94 mg (1 mmol) of phenol in 15 ml of acetone. Add to the solution, 290.8 mg of Ni(NO3)2·6 H2O (1 mmol) and a catalytic amount of p-toluenesulfonic acid (5 mg). Reflux the reaction for 30 min. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure (rotary evaporator), treat the residue with 20 ml of CH2Cl2, and wash the solution with water (20 ml) in a separatory funnel. Dry the organic layer (lower) on anhydrous sodium sulfate for several minutes. Then remove the desiccant by gravity filtration, filtering in a tared round-bottom flask. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure (rotary evaporator), weigh the solid, and calculate the yield (estimated yield 85 %, m.p. = 44-45 ºC). Optionally, purify by column chromatography using hexane:ethyl acetate (98:2) as eluent.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetone | 58.08 | -94 | 56 | 0.791 |
| CH2Cl2 | 84.93 | -97 | 40.0 | 1.33 |
| Ethyl acetate | 88.11 | -84 | 77.1 | 0.902 |
| Hexane | 86.18 | -95 | 69 | 0.659 |
| Na2SO4 | 142.04 | 884 | - | 2.630 |
| Ni(NO3)2·6H2O | 290.79 | 56 | 136.7 | 2.050 |
| Phenol | 94.11 | 40-42 | 182 | 1.07 |
| o-Nitrophenol | 139.11 | 45 | 214 | - |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate | 190.22 | 100-106 | - | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetone |   |
| CH2Cl2 |  |
| Ethyl acetate |   |
| Hexane |     |
| Na2SO4 | Non-hazardous |
| Ni(NO3)2·6H2O |     |
| Phenol |    |
| o-Nitrophenol |  |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetone | CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CH2Cl2 | YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Ethyl acetate | XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hexane | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Na2SO4 | PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Ni(NO3)2·6H2O | AOPCKOPZYFFEDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Phenol | ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| o-Nitrophenol | IQUPABOKLQSFBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| p-Toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate | KJIFKLIQANRMOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- V. Anuradha, P. V. Srinivas, P. Aparna, and J. Madhusudana Rao, p-Toluenesulfonic acid catalyzed regiospecific nitration of phenols with metal nitrates, Tetrahedron Letters 47 (2006), no. 28, 4933–4935, DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.05.017