Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 6, 2023
Objective
To perform a C−C coupling reaction (Suzuki reaction) in aqueous medium to obtain a bisphenyl derivative.
Background
The Suzuki reaction allows the formation of C−C bonds of type σ under mild conditions and with good yields from a boronic acid or ester and vinyl or aryl halide in basic medium, in the presence of Pd(0).
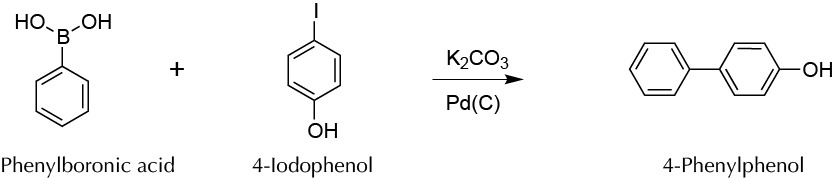
This reaction has been widely used to synthesize various polyolefins, styrene derivatives, and substituted biphenyls.
Experimental procedure
Add to a 50 ml round-bottom flask, in this order, 122 mg of phenylboronic acid, 414 mg of potassium carbonate, 220 mg of 4-iodophenol, and 10 ml of deionized water. Weigh in a suitably sized container 3 mg Pd on C 10 %, add 1 ml of deionized water, and stir gently by hand to form a slurry that is then transferred to the reaction flask.
| DANGER! “Carry out all experiments in fume cupboard”. |
Couple the flask to a water-jacketed condenser, and reflux the mixture on a hot plate with a magnetic stirrer vigorously for 30 min (until a precipitate appears). After this time, switch off the plate and allow to cool to r.t. Add HCl 2 M to an acidic pH (check with indicator paper). Separate the resulting solid, still containing the catalyst, by filtering with a Hirsch funnel. Wash the solid with 10 ml of water. Then, in a Hirsch funnel, add 10 ml of MeOH, and collect the filtrate in a clean container. Add to the resulting MeOH solution 10 ml of deionized water to obtain the precipitate of the product. Purify by recrystallization, heating in a water bath container with the precipitate and the MeOH/H2O mixture. If necessary, add 1 to 2 ml more of hot MeOH, to finish dissolving the solid. Filter under vacuum with a Hirsch funnel, air dry the solid (can recover the next day). Weigh and calculate the yield.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Phenylboronic acid | 121.93 | 216-222 | - | - |
| 4-Iodophenol | 220.01 | 92-94 | 138 | - |
| 4-Phenylphenol | 1170.21 | 164-166 | 321 | - |
| K2CO3 | 138.21 | 891 | - | - |
| Pd(C) | 106.42 | - | - | - |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| MeOH | 32.04 | -98 | 64.7 | 0.791 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Phenylboronic acid |  |
| 4-Iodophenol |   |
| 4-Phenylphenol |  |
| K2CO3 |  |
| Pd(C) | Non-hazardous |
| HCl |   |
| MeOH |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Phenylboronic acid | HXITXNWTGFUOAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 4-Iodophenol | VSMDINRNYYEDRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 4-Phenylphenol | YXVFYQXJAXKLAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| K2CO3 | BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Pd(C) | |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| MeOH | OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- E. Aktoudianakis, E. Chan, A. R. Edward, I. Jarosz, V. Lee, L. Mui, S. S. Thatipamala, and A. P. Dicks, “Greening up” the Suzuki reaction, Journal of Chemical Education 85 (2008), no. 4, 555, DOI: 10.1021/ed085p555