Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on May 2, 2024
What is Kucherov reaction?
The Kucherov reaction, also referred to as the Kucherov coupling or Kucherov condensation, involves the hydration of acetylenic hydrocarbons in the presence of a catalyst, such as mercuric sulfate HgSO4 or boron trifluoride BF3, and dilute sulfuric acid H2SO4, yielding ketones.
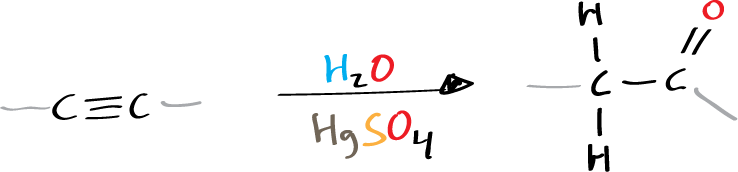
The Kucherov reaction is not commonly referred to by its name and is considered a rare reaction. Mechanistically, the reaction serves as an example of the electrophilic addition to an alkyne.
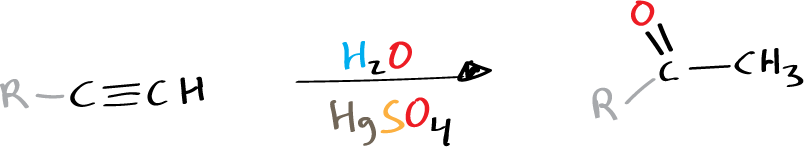
In line with Markovnikov’s rule, the reaction involves the addition of hydrogen (H⊕ or any other electrophilic part of a molecule) to the least substituted carbon, or the carbon atom with fewer hydrogen atoms.
References
Kutscheroff, M. (1881), Ueber eine neue Methode direkter Addition von Wasser (Hydratation) an die Kohlenwasserstoffe der Acetylenreihe. [On a new method of direct addition of water (hydration) to hydrocarbons of the acetylene series.] Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 14: 1540-1542. https://doi.org/10.1002/cber.188101401320