Gabriel synthesis
Synthetic procedures to obtain amines, such as the reduction of nitro, azido and cyano groups or SN2 reactions in which an amine acted as a nucleophile, have been described in other sections.
Gabriel synthesis is a method of obtaining amines, mainly primary, in two steps, starting from alkyl halides and using potassium phthalimide, which is converted in a first step into the cyclic tertiary amide (SN2 reaction).
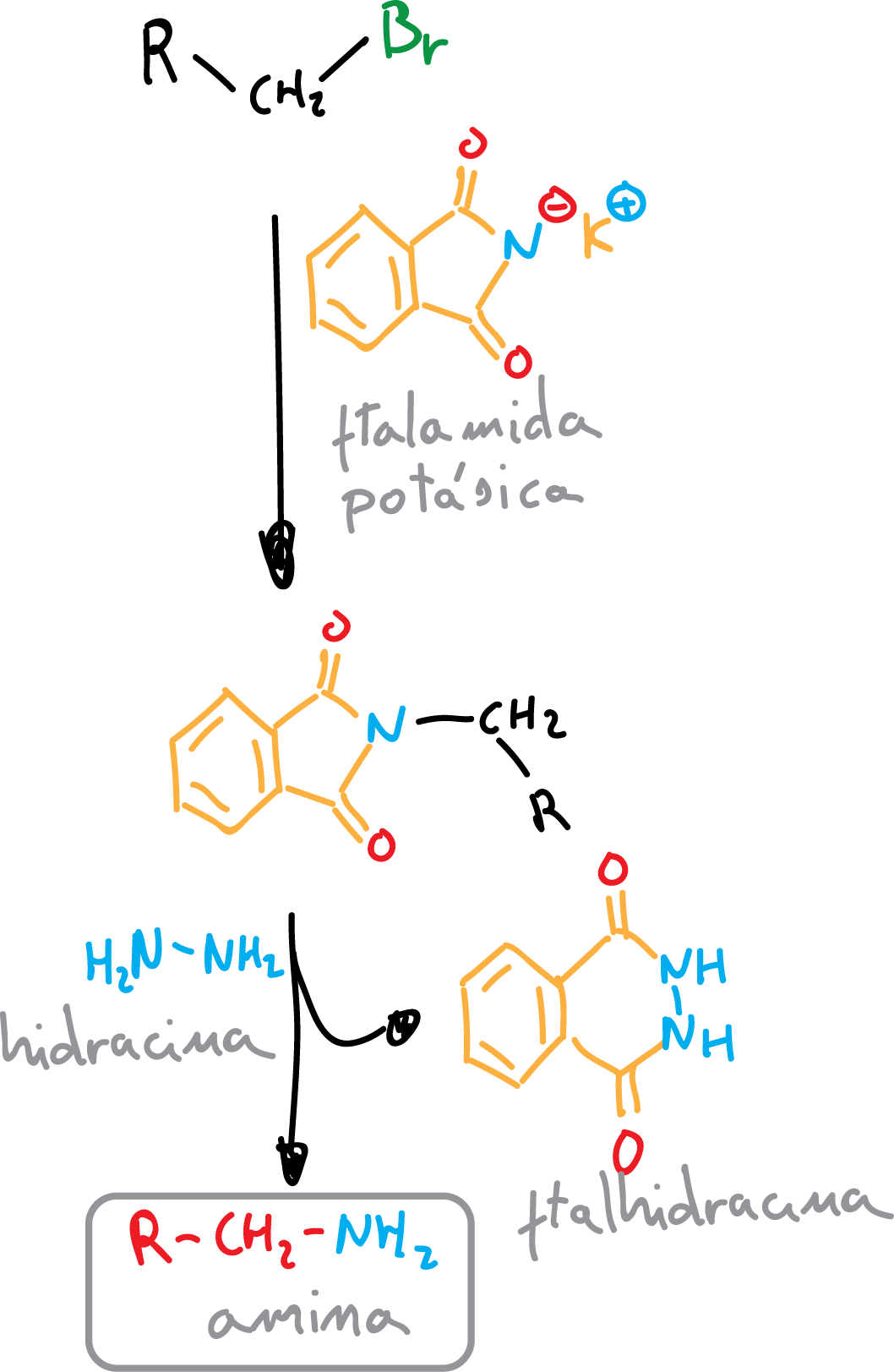
Further reaction with hydrazine gives as a by-product phthalhydrazide and an amine depending on the starting alkyl halide. Since the first reaction step is a SN2, primary halides without steric hindrance react better.
Alkylation
Amines, thanks to their unshared electron pair, can react with electrophiles such as haloalkanes (RX). Ammonia reacts with 1 mol of RX to give primary amines.
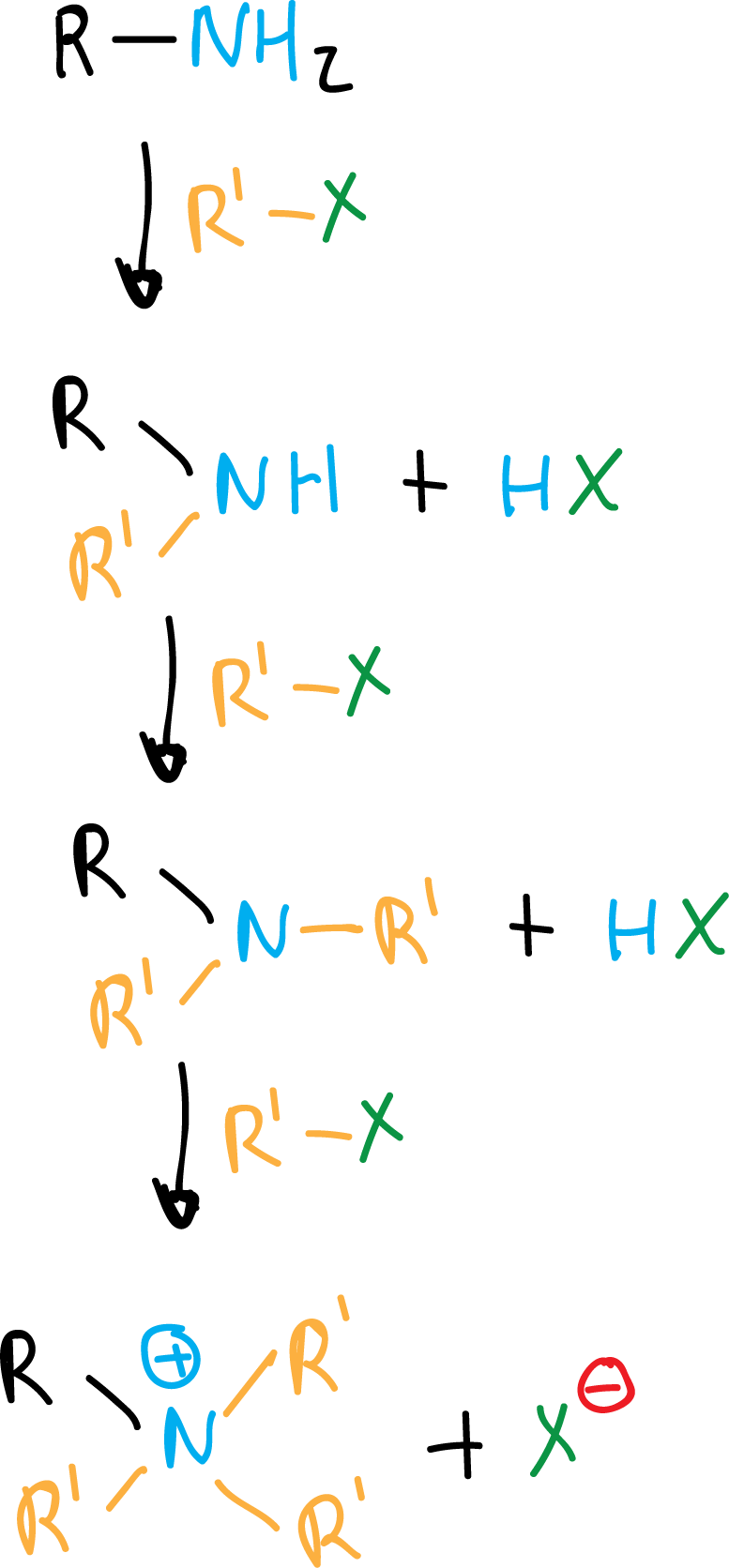
If there is an excess of alkylating agent, they react again and are converted into secondary amines, and the latter are also transformed into tertiary amines and, finally, into quaternary ammonium salts.
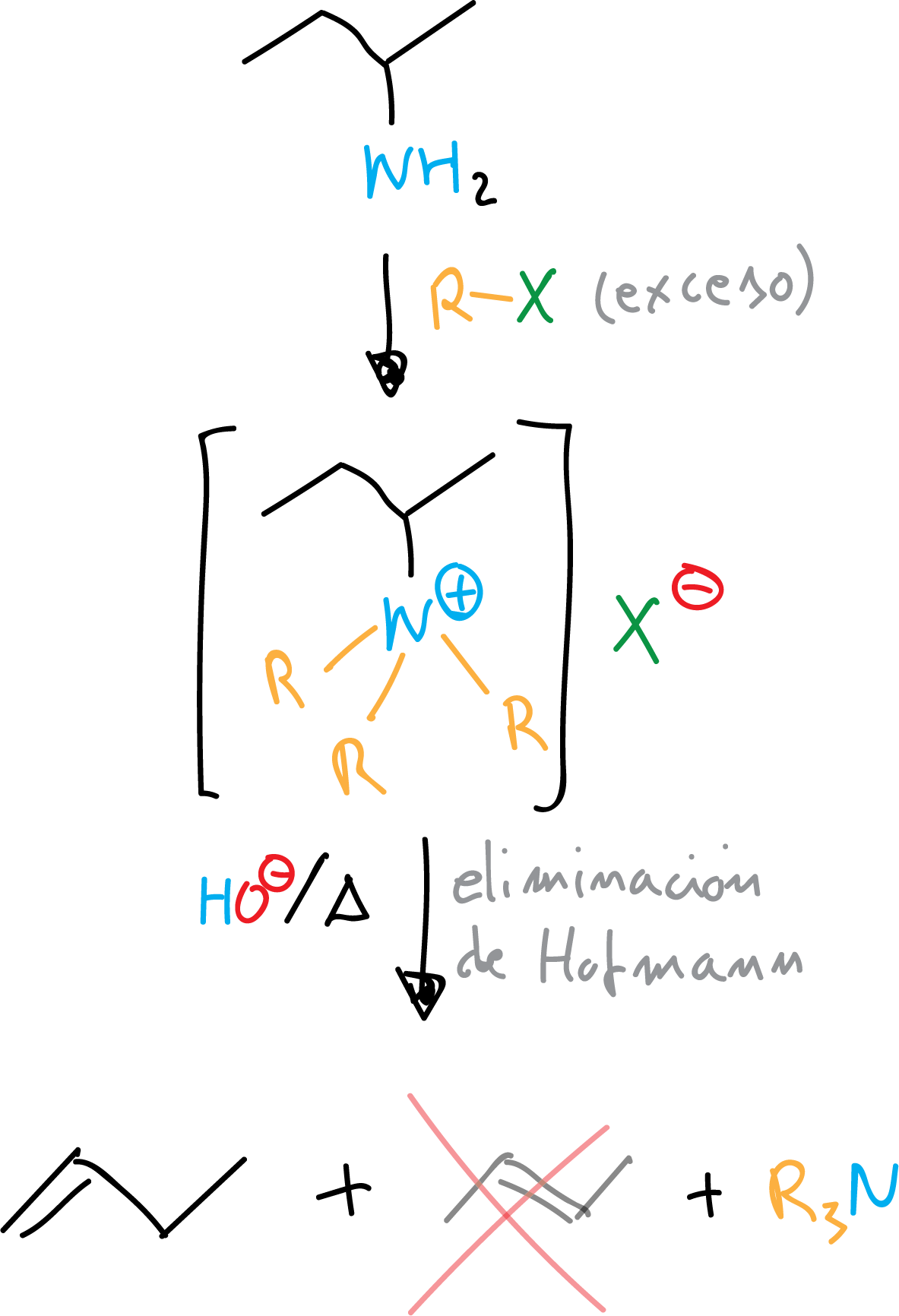
Hofmann elimination
With an excess of RX in the alkylation reaction any type of amine can be transformed into quaternary ammonium salt. These salts, in basic media, undergo Hofmann elimination to give an alkene (the least substituted) and tertiary amine.
Conversion to amides and sulfonamides
Other electrophiles that react with amines are acyl chlorides and sulfonic acid chlorides to give amides and sulfonamides, respectively.
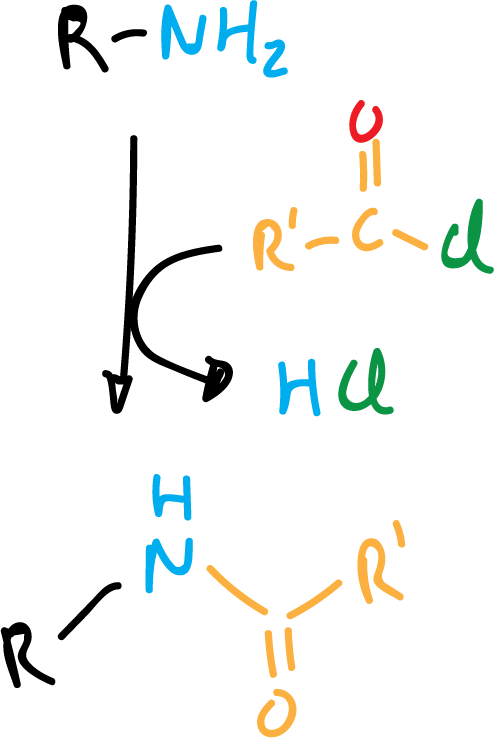
With secondary amines the reaction is as shown in the following scheme:
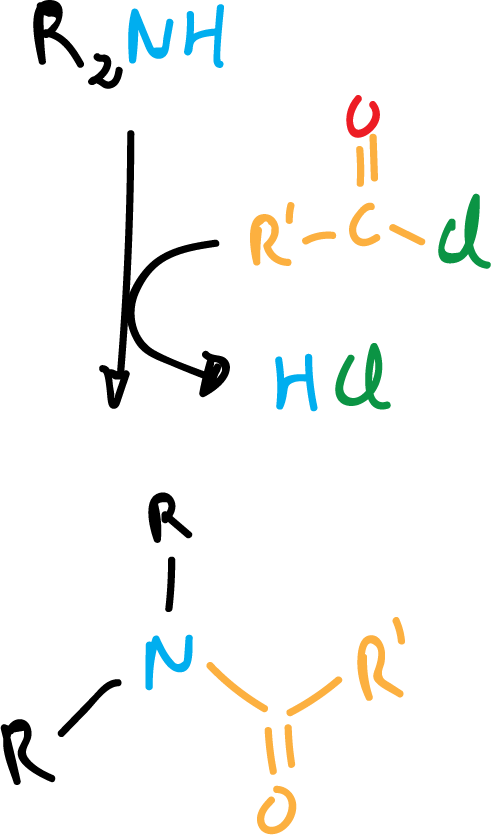
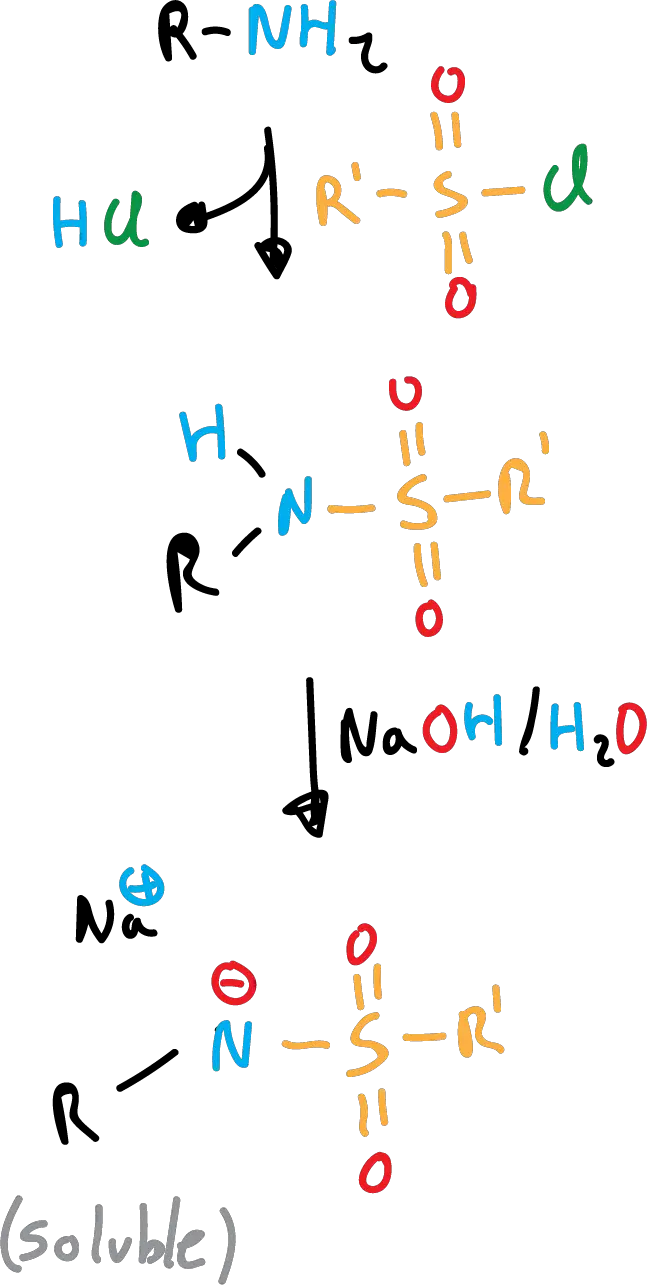
The Hinsberg test to identify primary and secondary amines is based on the different solubility of sulfonamides in basic media.
Primary sulfonamides are soluble due to anion formation (loss of the nitrogen proton).
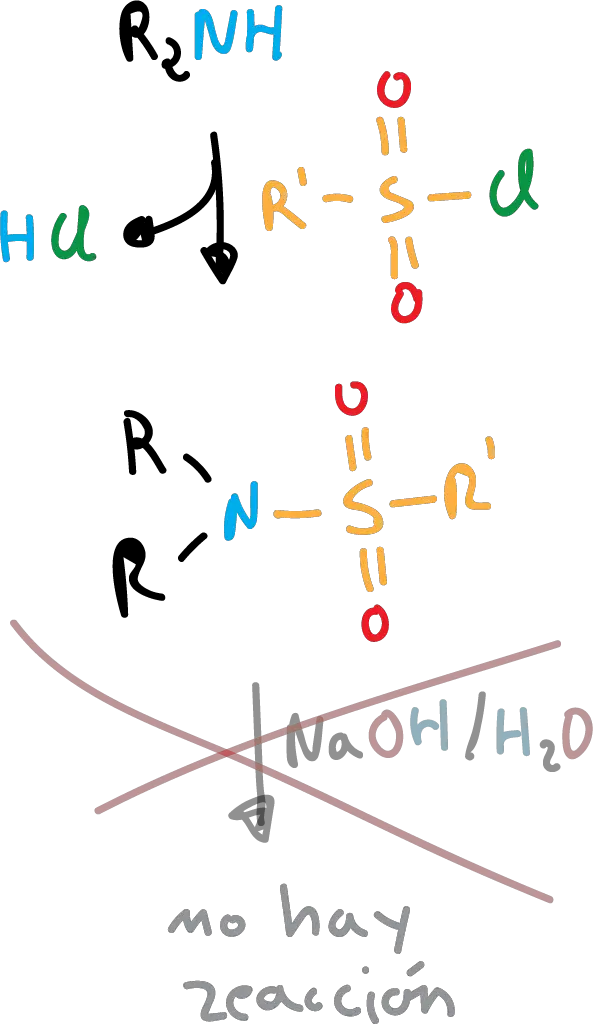
However, secondary amines are insoluble because they do not possess the proton. Tertiary amines do not react with sulfonamides.
Reactions with nitrous acid
Nitrous acid (HNO2) is another nucleophile that reacts with primary aliphatic amines to give diazonium salts that are subsequently transformed into a mixture of alcohols and alkenes.
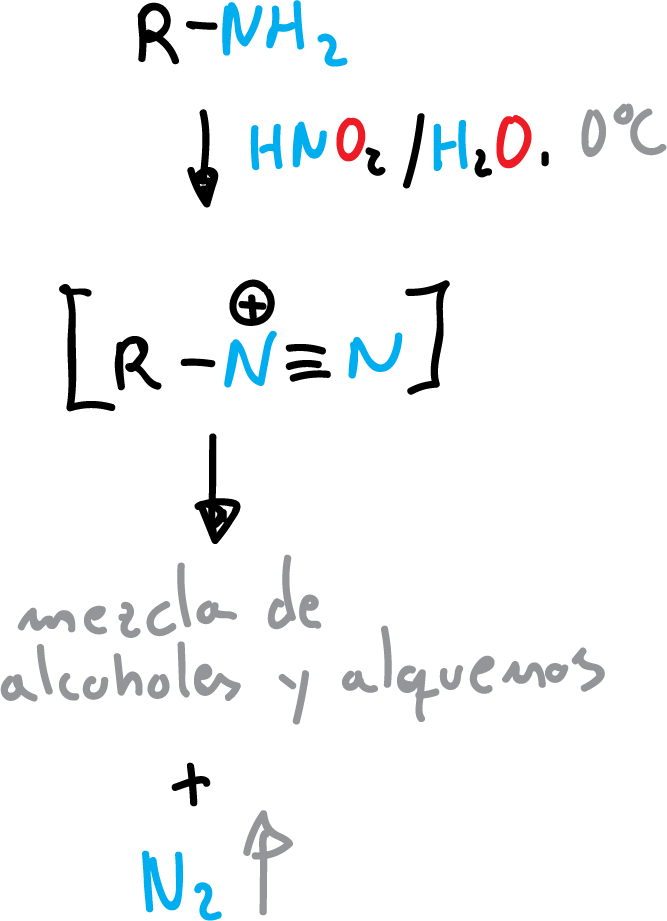
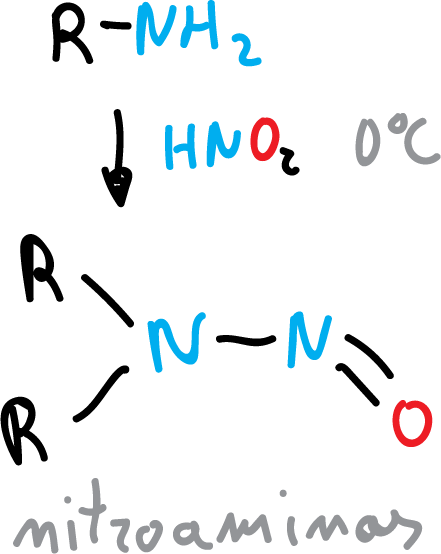
It also reacts with secondary amines to give N-nitrosamine.
Nitrous acid is prepared from sodium nitrite (NaNO2) and HX.
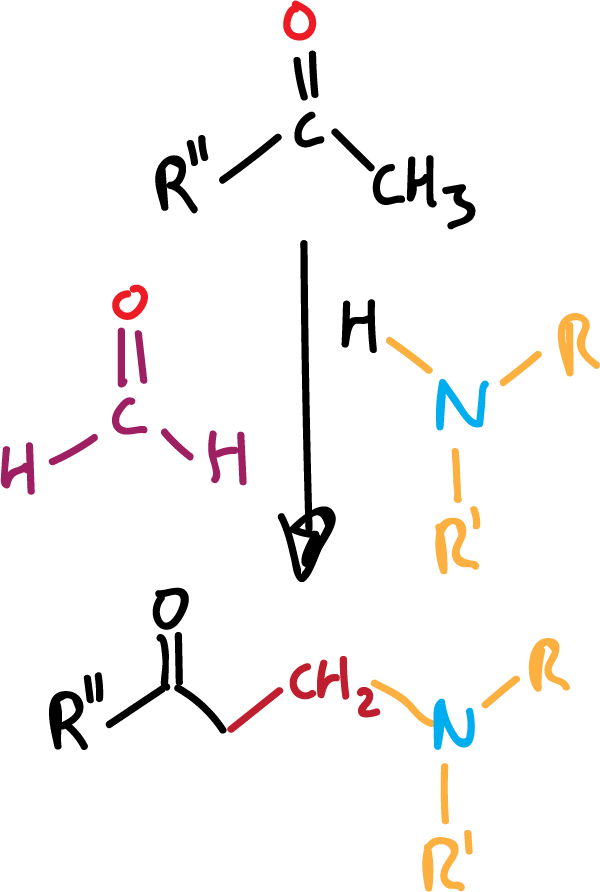
Mannich reacction
Although it is a condensation reaction (see reactions of enols and enolates), and uses formaldehyde (see reactions of aldehydes and ketones) to lengthen the carbon chain of the product by one methylene, it will be discussed here, since it uses and allows obtaining aliphatic amines.
It is certainly a versatile reaction for converting simple amines into more complex ones. Three reagents are used, an enolizable carbonyl compound, formaldehyde and an amine, and it gives us the condensation product of all three, as indicated in the general reactivity scheme.