Written by J.A Dobado | Last Updated on April 22, 2024
Objective
To study the oxidative coupling of alkynes with the Glaser-Eglinton-Hay coupling; with is the oldest of the acetylenic couplings.
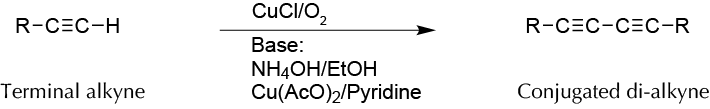
Background
Glaser-Eglinton-Hay coupling involves the reaction of the ethylenic compound with cuprous salts in the pres- ence of oxygen and a base (ammonia initially). Subsequent modifications to this reaction changed the reaction conditions (reagents and bases used). It is assumed that the reaction mechanism proceeds via radical and copper(I) acetylide. Thus, the Glaser-Eglinton-Hay coupling is a modification in which two terminal alkynes are coupled directly, using a copper(II) salt, such as copper acetate and pyridine as a base.
Experimental procedure
In a two-necked flask provided with agitation, put 30 ml of propan-2-ol, 100 mg of CuCl, and 20 drops of tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA). Put in one of the openings a reflux condenser, and in the other an adapter provided with a pipette bubbling oxygen into the solution. Add 2 g of 1-ethynylcyclohexanol and reflux the reaction for 30–40 min. Verify the absence of starting material by TLC, hexane/ethyl acetate (7:3).
Remove all propane-2-ol in a rotary evaporator. Then add 20 ml of water containing 1 ml of concentrated HCl. Cool and filter the product. If the product is blue or green, return to add HCl/water to remove all copper salts. If it has a dark color, dissolve in hot ethyl acetate and discolor with activated carbon. If it is almost white, recrystallize with ethyl acetate, and dry with an air stream through the same Büchner.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| 1-Ethynylcyclohexan-1-ol | 124.18 | 30.0-33.5 | 180 | - |
| CuCl | 99.00 | 430 | 1490 | 4.140 |
| Ethyl acetate | 88.11 | -84 | 77.1 | 0.902 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| O2 | 32.00 | -218 | -183 | - |
| Propan-2-ol | 60.10 | -89.50 | 82 | - |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine | 116.20 | -55 | 120-122 | 0.775 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| 1-Ethynylcyclohexan-1-ol |  |
| CuCl |   |
| Ethyl acetate |   |
| HCl |   |
| O2 |   |
| Propan-2-ol |   |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine |    |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| 1-Ethynylcyclohexan-1-ol | QYLFHLNFIHBCPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CuCl | OXBLHERUFWYNTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Ethyl acetate | XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| O2 | MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Propan-2-ol | KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine | FGNGTWFJQFTFGN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Hutchison, J. E., Doxsee, K. M. (2004). Green Organic Chemistry: Strategies, Tools, and Laboratory Experiments. Austria: Thomson-Brooks/Cole. ISBN: 9780534388515