Objective
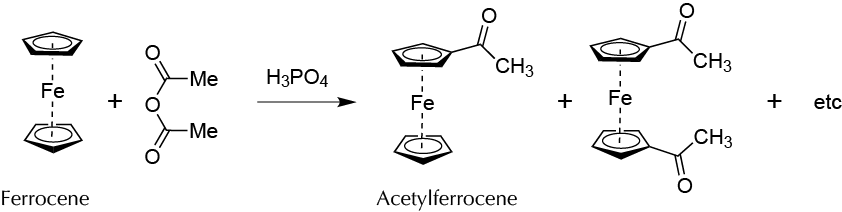
To prepare acetylferrocene by electrophilic substitution on one of the cyclopentadiene rings of ferrocene (bis(η5-cyclopentadienyl) iron(II)).
Background
The serendipitous discovery, in 1951, of ferrocene opened an entire, new area of research and contributed greatly to the technological advance of Chemistry. Among the uses and applications of ferrocene, the following bear noting:
- Aviation fuel catalyst, improving the rate of burning of up to 4-fold and lowering the temperature of the exhaust pipes.
- Additive to gasoline, for antiknock, instead of lead compounds.
- Additive to fuel oil to eliminate fumes and waste.
- Catalyst in ammonia synthesis under mild conditions.
- Additive in the manufacture of polymers as a protective agent and stabilizer against heat or UV radiation.
- Component of photosensitive materials, replacing the silver in films, photocopying, and printing with high resolution.
- Fertilizer production.
Ferrocene as any aromatic substance can undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (SEAr) reactions.
Procedure
In a test tube, mix 0.4 g of ferrocene, 2 ml of acetic anhydride, and 0.5 ml phosphoric acid. Heat the mixture in a water bath at 60 ºC for 5 min.
| DANGER! “The acetic anhydride reacts violently with water and the mixture may splatter.” |
Add a quantity of crushed ice equal to the volume of the reaction, stirring until the ice melts; remove the suspension adding hexane (2 × 5 ml); stir the mixture using a Pasteur pipette; and separate the organic layer. Collect the organic layer in another test tube and dry by adding anhydrous sodium carbonate.
At this point, make a TLC using as eluent hexane/diethyl ether (1:1). An orange stain will appear with an observed Rf value of approximately 0.3, generated by the reaction product, and probably another yellow one with Rf value of approximately 0.8, corresponding to unreacted ferrocene. Purify the reaction crude by CC using 5 g of silica gel. For this, prepare 75 ml of eluent hexane/diethyl ether (4:1) and a rack with 15 test tubes.
Prepare the sample to be purified by adding 0.5 g of silica gel to the reaction crude and remove the solvent under reduced pressure (rotary evaporator). This will produce an orange solid, which is to be placed into the CC column. Collect the eluent in fractions of approximately 5 ml in each test tube.
Check the nature and purity of the fractions collected, using TLC under the same conditions described above. Collect the tubes containing the acetylferrocene in a tared round-bottom flask, and remove the solvent under reduced pressure (rotovap) to give a solid of m.p. = 85–86 ºC.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Acetic anhydride | 102.09 | -73.1 | 139.8 | 1.080 |
| H3PO4 | 98.00 | 40 | 158 | 1.685 |
| Hexane | 86.18 | -95 | 69 | 0.659 |
| Na2CO3 | 105.99 | 851 | - | 2.532 |
| Diethyl ether | 74.12 | -116 | 34.6 | 0.71 |
| Silica gel (SiO2) | 60.09 | - | - | - |
| Ferrocene | 186.03 | 172-174 | 249 | - |
| Acetylferrocene | 228.07 | 81-83 | - | - |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Acetic anhydride |    |
| H3PO4 |  |
| Hexane |     |
| Na2CO3 |  |
| Diethyl ether |   |
| Silica gel (SiO2) | Non-hazardous |
| Ferrocene |   |
| Acetylferrocene |  |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Acetic anhydride | WFDIJRYMOXRFFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| H3PO4 | NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Hexane | VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Na2CO3 | CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| Diethyl ether | RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Silica gel (SiO2) | VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Ferrocene | KTWOOEGAPBSYNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Acetylferrocene | PHMAOJNZIFULOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145